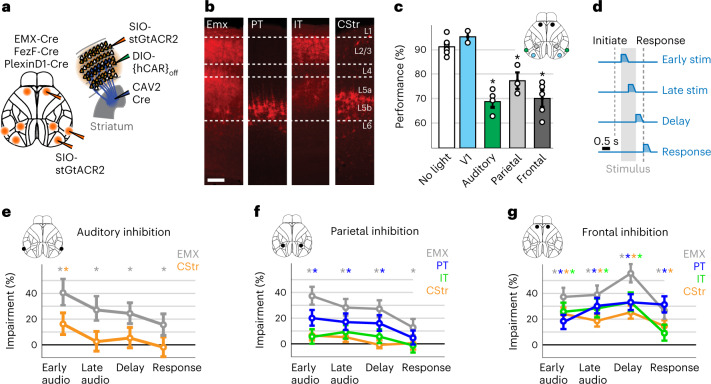
Fig. 8. Temporally restricted, pyramidal neuron-specific inactivation of parietal and frontal cortex disrupts decisions.
a, Left, schematic of injection scheme to induce stGtACR2 expression in EMX, IT or PT neurons. V1 injections were performed in a subset of EMX mice. Right, intersectional viral approach for targeting CStr neurons. A mixture of AAV-DJ-hSYN-DIO-{hCAR}off and AAV1-SIO-hSyn1-stGtACR2-FusionRed was injected into the cortex to enhance CAV-2-Cre uptake, subsequently inducing stGtACR2 expression in CStr neurons. b, Laminar distribution of stGtACR2-FusionRed in EMX, PT, IT and CStr neurons. c, Behavioral performance (percentage correct) of EMX mice during inactivation of V1 (n = 2 mice), auditory (n = 5 mice), parietal (n = 3 mice) or frontal (n = 5 mice) cortex. Data are presented as the mean ± s.e.m. Circles denote individual mice. d, Schematic of optogenetic inactivation paradigm; 0.5-s-long optogenetic inhibition was performed during the first or last half of the stimulus period, the subsequent delay or the response period. Light power ramped down after 0.3 s. e, Behavioral impairment (percentage change from control performance) with inhibition of EMX or CStr neurons in auditory cortex. Circles denote mean impairments, and error bars represent 95% confidence intervals. nEMX = 702, nCStr = 834 trials. f, Behavioral impairments from parietal PyN-type-specific inhibition. Conventions as in e. nEMX = 1,627, nPT = 1,082, nIT = 890, nCStr = 1,033 trials. g, Behavioral impairments from parietal PyN-type-specific inhibition. nEMX = 1,888, nPT = 1,304, nIT = 791, nCStr = 1,372 trials. Conventions as in f. Asterisks indicate Bonferroni-corrected P < 0.01, two-sided binomial test.