Figure 1.
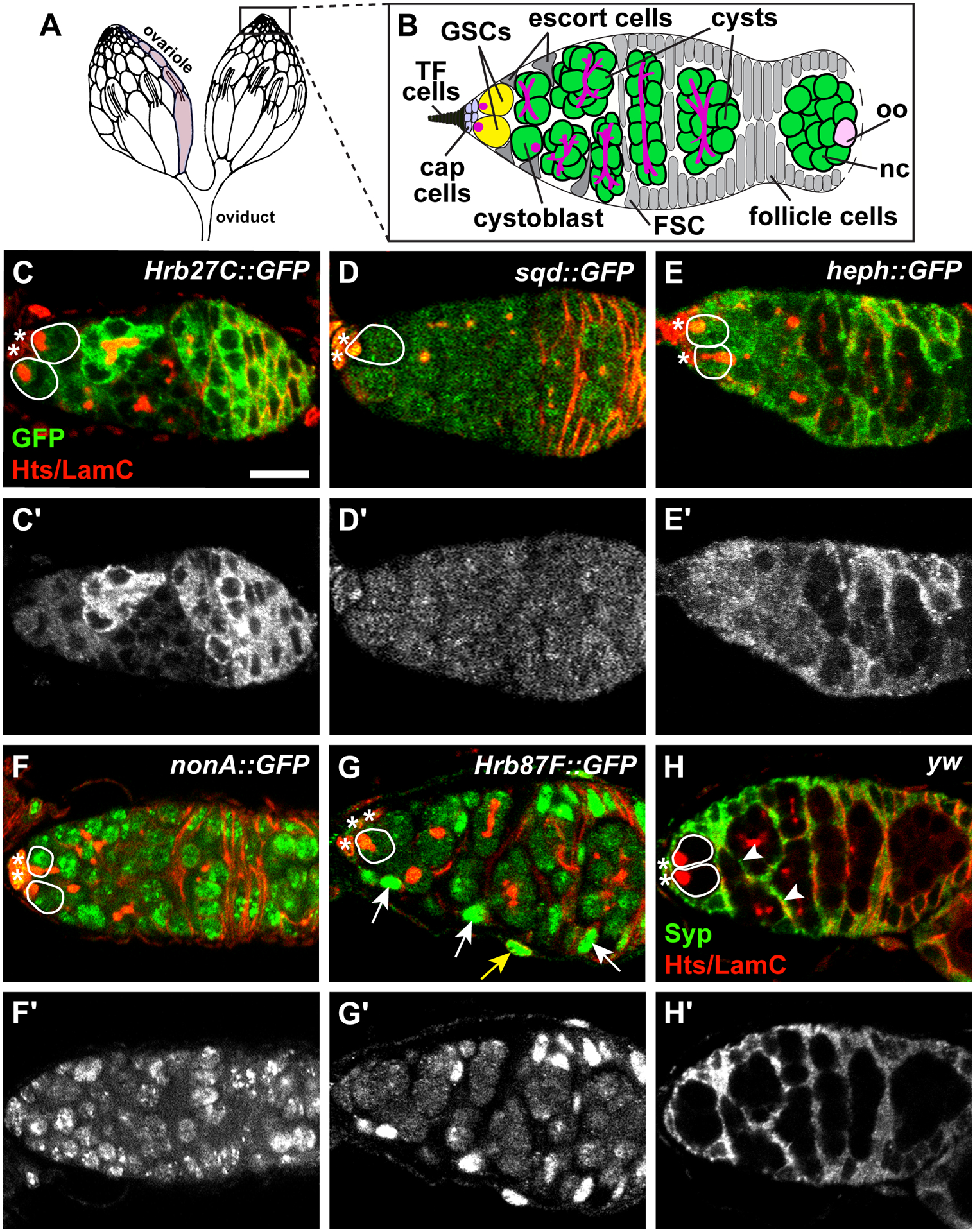
Drosophila hnRNPs are expressed in distinct patterns in the germarium. (A-B) The ovary (A) is composed of 15–20 ovarioles (one ovariole is shaded in light gray). At the anterior tip of each ovariole is a germarium (B), where germline stem cells (GSCs; yellow) are anchored to a somatic niche (light blue) composed of cap cells and terminal filament (TF) cells. GSCs divide asymmetrically to form cystoblasts (green) which divide mitotically four times with incomplete cytokinesis, forming cysts (green). One cell in the cyst becomes the oocyte (oo, pink); the other 15 become nurse cells (nc, green). Germ cells are characterized by the presence of a fusome (magenta), which extends as germ cells divide. Somatic escort cells (gray triangles) signal to germ cells to promote differentiation. Follicle stem cells (FSC; gray) give rise to follicle cells (gray) which surround the 16-cell germline cyst, giving rise to an egg chamber that buds off the germarium. (C-H) Representative germaria from GFP-tagged hnRNP transgenic flies labeled with anti-GFP (C-G) or wild-type flies labeled anti-Syp (H) and counterstained with anti-Hts+anti-LamC (red; fusomes, follicle cell membranes, and cap cell nuclear envelopes). Grayscale images of the corresponding green channel alone in C’-H’. Solid white lines demarcate GSCs; asterisks represent cap cells. Somatic cell nuclei (arrows) or membrane extensions (arrowheads) are indicated in G-H. The yellow arrow in G points to an ovarian sheath cell nucleus. Scale bar = 10 μm.
