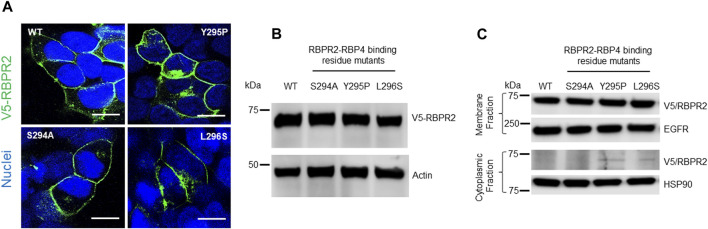
FIGURE 3.
Cellular localization and expression of WT-RBPR2 and RBPR2-mutants.(A) Transient expression and staining of mouse V5-tagged WT-RBPR2 and variants in NIH3T3 cells using the V5-antibody. Nucleus, DAPI, blue; RBPR2-V5, Green. Scale bar = 50 μm. (B) Protein expression and representative western blot images of WT-RBPR2 and RBPR2-mutant proteins, which affect the “SYL” domain; anti-Actin = protein loading control. (C) Subcellular fractionation of stable cells expressing WT-RBPR2 or individual RBPR2-RBP4 mutants. Stable NIH3T3/LRAT cells expressing either WT-RBPR2 or individual RBPR2-RBP4 binding residues mutants were fractionated as outlined in the methods. Normalized portions of each extract (∼30 μg) were analyzed by Western blotting using antibodies against proteins from cytoplasmic (HSP90) and plasma membrane (EGFR).