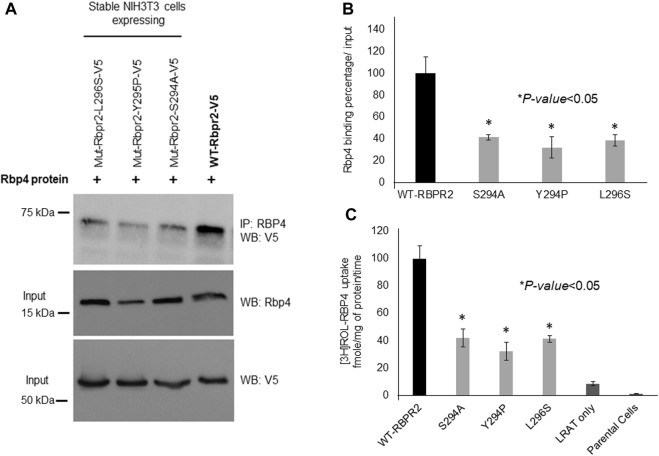
FIGURE 4.
Extracellular RBP4 binding capabilities of RBPR2 and Vitamin A uptake assays. (A,B) Co-IP experiments showed a strong interaction between wild type (WT) RBPR2 and exogenous applied human RBP4 protein. Conversely, mutants targeting the proposed RBP4 binding sites on RBPR2, showed weaker interaction with RBP4 (62%–73% decreased binding capability compared to WT-RBPR2; p < 0.05). (C) Compared to NIH3T3/LRAT/WT-RBPR2 expressing cells, all NIH3T3/LRAT/RBPR2-mutant expressing cells showed decreased ability (<81% of WT-RBPR2 activity; *p < 0.05) to uptake extracellular applied [3H]ROL bound RBP4.