Fig. 6. HDAC6 modulates the acetylation level of MYC.
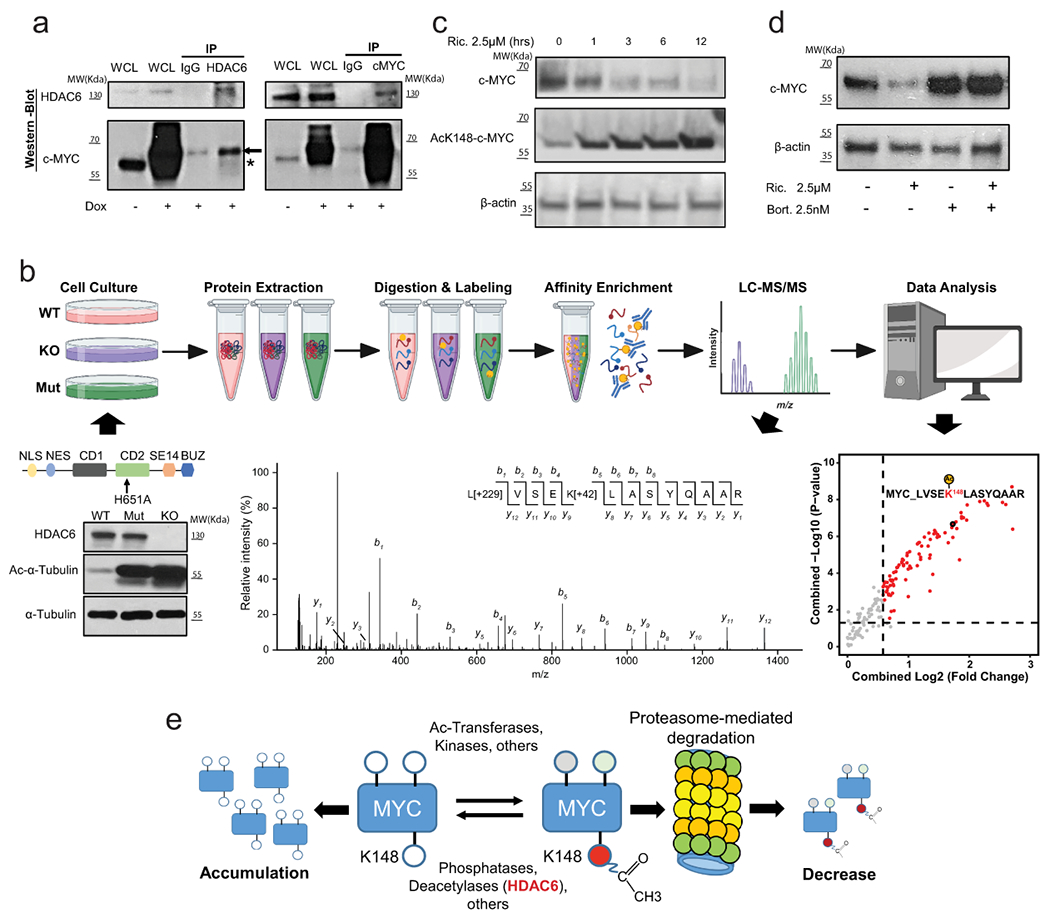
(a) Co-IP of MYC and HDAC6 in HEK-293T cells. The asterisk and arrow indicate the endogenous and the transduced c-MYC respectively (transduced construct expresses a slightly larger form). IP results were reproduced n=3 times from independent experiments. (b) Schematic description of the proteomic study described in the text. The WT-blot shows the accumulation of acetylated α-Tubulin in HDAC6 deficient HAP1 cells. The MS/MS spectrum shows an example assigned to the peptide containing MYC K148 acetylation site with b- and y- ions corresponding to the N- and C-terminal fragments, respectively. Peaks that match to theoretically calculated fragmented ions of the lysine-acetylated peptide are indicated. Modifications on specific residuals are indicated for TMT (+229 Da) and acetylation (+42 Da), respectively. WT-blot results were reproduced n=3 times from independent experiments. The dot plot shows the top differentially acetylated proteins from the proteomic study. The vertical and horizontal dash lines indicated the cutoffs of fold change > 1.5 and P < 0.05, respectively. N = 2 for each group. P value was estimated using two-tailed t test. (c) Degradation of MYC correlates with the accumulation of the ac-K148 form during treatment of MDA-MB-453 with ricolinostat (2.5μM). WT-blot results were reproduced n=3 times per time point from independent experiments. (d) Proteasome inhibition by Bortezomib (2.5nM) blocks the reduction of c-MYC protein induced by ricolinostat (2.5μM). WT-blot results were reproduced n=3 times per drug combination from experimental replicates. (e) Mechanistic model of the effect of HDAC6 inhibition on MYC expression. C-MYC stability is influenced by posttranslational modification. Acetylation of K148 promotes degradation by the proteasome and it is prevented by HDAC6. Thus, HDAC6 inhibition leads to hyperacetylation of MYC leading to its degradation.
