Figure 1 – Mif2-PEST region phosphorylation supports kinetochore function.
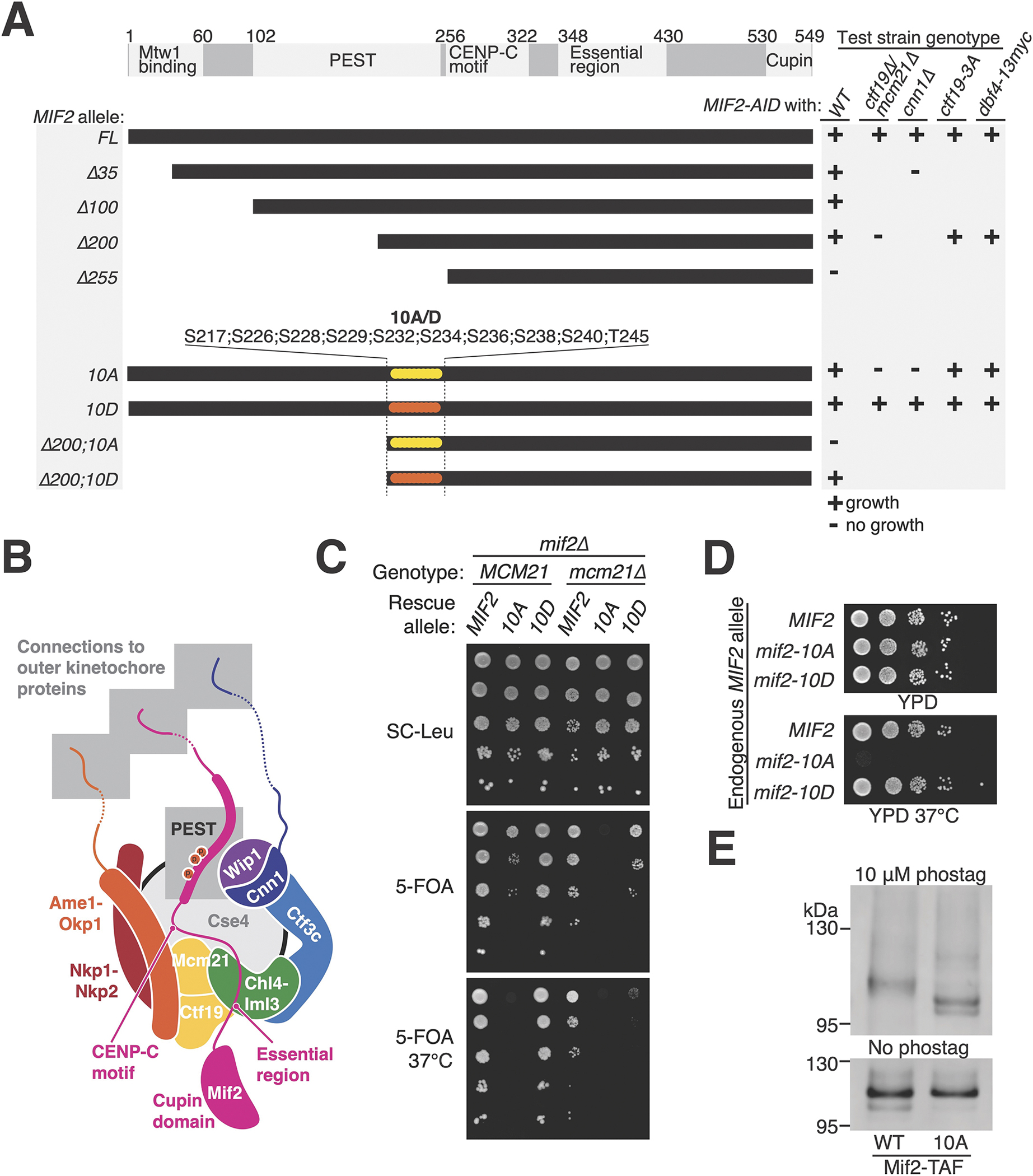
(A) MIF2 genetic complementation experiments. Rescue plasmids coding for MIF2 or its mutants (CEN/ARS-LEU2 MIF2; listed at left) were tested for their ability to complement depletion of endogenous Mif2-AID protein in strains with the indicated genotypes (listed at right). See also Figure S1 and S2. (B) Illustration of the inner kinetochore. Shaded boxes show three peptides that recruit outer kinetochore proteins (top) and the phosphorylated Mif2-PEST (middle). (C) Synthetic lethal interaction between mcm21Δ and mif2-10A. mif2Δ (left) or mif2Δ mcm21Δ (right) cells carried the indicated MIF2 rescue allele on a test plasmid (CEN/ARS-LEU2 with MIF2, mif2-10A, or mif2-10D). A second complementing plasmid (CEN/ARS-URA3 with MIF2 or both MCM21 and MIF2) was ejected by growth on 5-FOA (middle and bottom), leaving only the test plasmid. (D) Heat stress (37 °C) kills mif2-10A mutant cells. MIF2, mif2-10A, or mif2-10D were integrated into the native MIF2 locus in otherwise wild type cells. (E) Mif2-TAF was purified from asynchronous cultures, resolved by SDS-PAGE with 10 μM (top) or 0 μM (bottom) Phos-tag acrylamide, and detected by anti-protein A Western blot (TAF: 6xHIS-3xFLAG-ProteinA tag). See also Figure S3A and Tables S1–2.
