Figure 4 – Mif2-PEST mutation interferes with Mif2-Cse4 association in vivo.
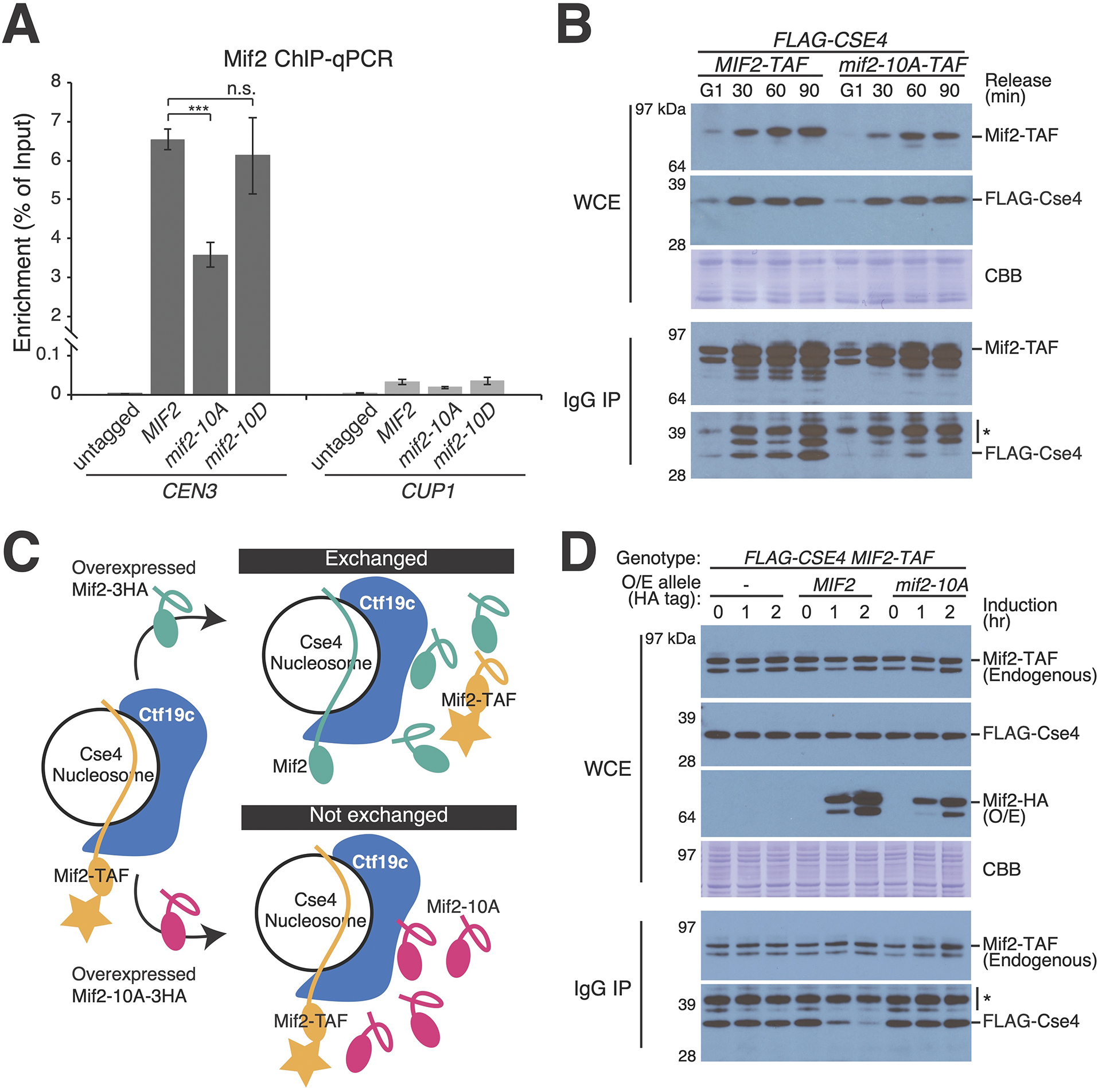
(A) Measurement of Mif2-CEN3 association in asynchronous cells with the indicated MIF2 alleles coding for Mif2-TAF proteins. ChIP-qPCR for Mif2-TAF is shown. Mif2 association with a non-centromeric locus (CUP1) is shown at right (*** p < 0.001, Student’s t-test). (B) Co-purification of Mif2 and Cse4 analyzed during cell cycle progression. Cells were arrested in G1 with alpha factor and released into the cell cycle for the indicated amounts of time (top). Mif2-TAF was immunopurified. Co-purifying FLAG-Cse4 was detected by Western blot (WCE – whole cell extract; IgG IP – Mif2-TAF immunoprecipitation; CBB – Coomassie brilliant blue for total protein; * – background from partially degraded Mif2 protein A tag). (C) Schematic showing the experimental design for competition pull-down experiments (panel D). Upon induction of Mif2-HA expression from an ectopic locus, endogenous Mif2 (Mif2-TAF) was affinity-purified, and copurifying Cse4 was detected by Western blot. See also Figure S4A. (D) Overexpressed Mif2 but not Mif2-10A competes with endogenous Mif2 for Cse4 binding. Pulldown experiments were performed as in panel A. Time elapsed after induction of extragenic Mif2-WT or Mif2-10A is shown (O/E – overexpression; * – background band). See also Figure S4B and Tables S1–2.
