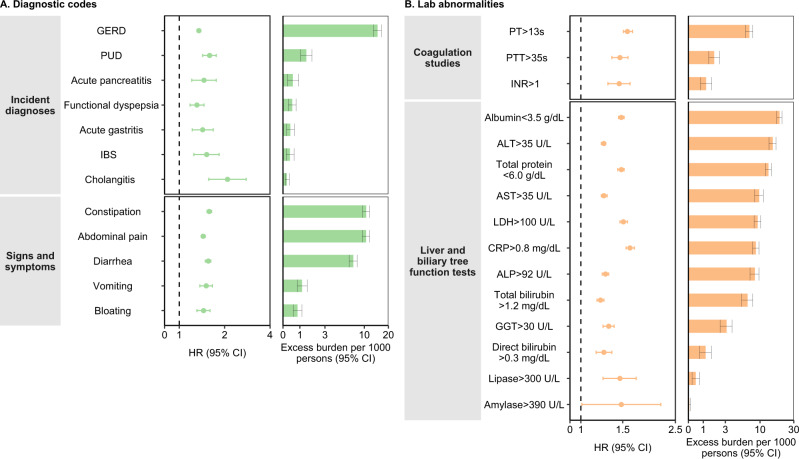
Fig. 1. Risks and 1-year burdens of incident post-acute COVID-19 gastrointestinal outcomes compared with the contemporary control cohort.
Outcomes were ascertained 30 d after the COVID-19-positive test until the end of follow-up. COVID-19 cohort (n = 154,068) and contemporary control cohort (n = 5,638,795). Panel A describes the risks and burdens of incident diagnoses (light green) and panel B describes the risks and burdens of incident laboratory abnormalities (orange). Adjusted HRs (dots) and 95% (error bars) CIs are presented, as are estimated excess burdens (bars) and 95% CIs (error bars). Burdens are presented per 1000 persons at 12 months of follow up. The dashed line marks a HR of 1.00; lower limits of 95% CIs with values greater than 1.00 indicate significantly increased risk. GERD, gastroesophageal reflux disorder; IBS irritable bowel syndrome, PT prothrombin time, PTT partial thromboplastin time, INR international normalized ratio, ALT alanine transaminase, AST aspartate transaminase, LDH lactate dehydrogenase, CRP c-reactive peptide, ALP alkaline phosphatase, GGT γ-glutamyl transferase.