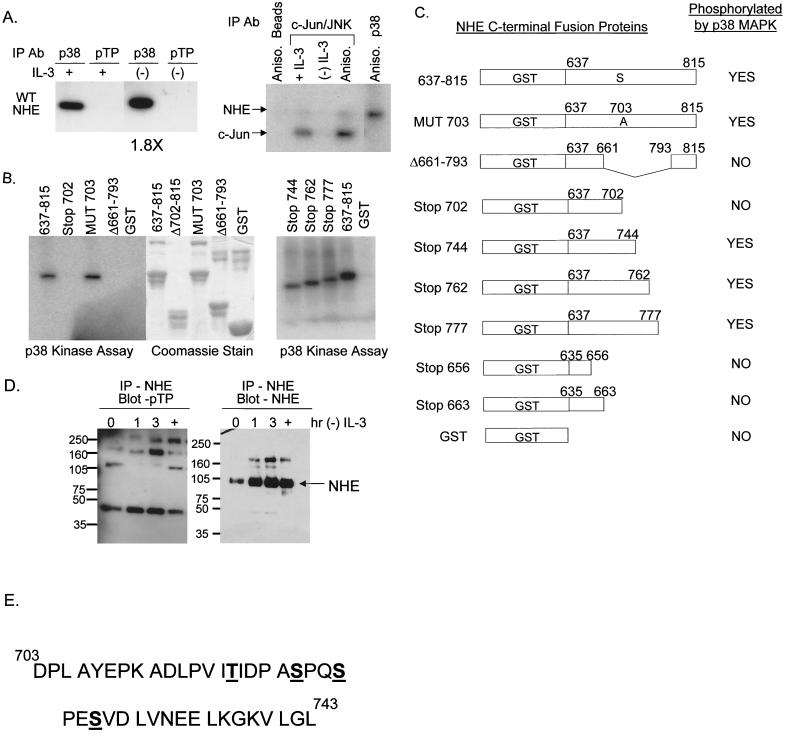
FIG. 7.
Kinase assays demonstrate that p38 MAPK directly phosphorylates NHE1 at a site(s) between amino acids 703 and 793. The numbering system used corresponds to the rabbit NHE1 sequence. (A) Protein lysates from FL5.12A cells cultured with or without IL-3 for 2 h were immunoprecipitated with either an antibody specific for phospho-p38 MAPK (p38) or an antibody specific for the motif, p-TP, and the ability of these kinases to phosphorylated the WT NHE-GST fusion protein was evaluated by an in-gel kinase assay as described in Materials and Methods. Only p38 phosphorylated the WT NHE-GST fusion protein, an activity which increased 1.8-fold during IL-3 withdrawal (left panel). Protein lysates from FL5.12A cells were also immunoprecipitated with c-Jun fusion beads to capture JNK, which was tested in an in vitro kinase assay for its ability to phosphorylate the WT NHEGST fusion protein. Unlike p38 MAPK, JNK did not phosphorylate NHE (right panel). (B) Protein lysates extracted from anisomycin-activated FL5.12A cells were immunoprecipitated with antibody to phospho-p38 MAPK and a kinase assay performed as described in Materials and Methods using the WT NHE-GST fusion protein and seven mutant NHE-GST fusion proteins as substrates. GST alone was included as a negative control. (C) The results of the kinase assay from panel B are summarized in table form. In addition, phospho-p38 MAPK did not phosphorylate NHE-GST fusion proteins containing amino acids 635 to 663. Possible phosphorylation sites by p38 MAPK on NHE are located in the region from amino acids 703 to 743, which excludes the proposed p90RSK phosphorylation site (Serine 703, numbering from human NHE1 sequence). (D) FL5.12A cells, cultured without IL-3 for 0, 1, 2, and 3 h or treated with anisomycin (+), were lysed, and the precleared protein extracts were immunoprecipitated with the A7 antibody specific for NHE1 and then run on an 8% Tris-glycine SDS gel and analyzed by Western blotting with the p-TP-specific antibody (left panel). The same blots were then reprobed with a commercially available anti-NHE1 antibody (right panel). NHE1 did not contain an activated p-TP motif. (E) Mass spectrometry analysis, as described in Materials and Methods, identified four sites at Thr 717, Ser 722, Ser 725, and Ser 728 as in vitro targets for p38 MAPK activity. Phosphorylation of one or more of these sites by p38 MAPK modulates alkalinization mediated by NHE during trophic factor withdrawal.