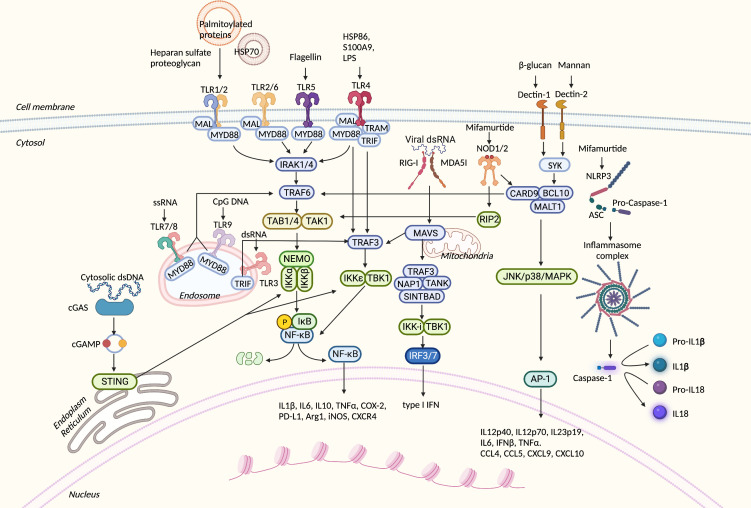
Figure 2.
Overview of PRR-related signaling pathways in myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs). PRRs can sense numerous danger signals released by pathogens and damaged normal and neoplastic cells. After binding to proper ligands, PRRs recruit adaptor proteins and trigger downstream signal transduction. These processes result in the translocation of transcription factors into the nucleus, expression of inflammatory-related genes, or direct cytokine activation from their inactive forms. PRRs, pattern recognition receptors; TLR, Toll-like receptor; HSP70, heat shock protein 70; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; S100A9, S100 calcium-binding protein A9; MyD88, myeloid differentiation primary TAK-binding proteins 1; IKK, IκB kinase; NEMO, NF-κB essential modulator; Mal, MyD8response 88; RIP2, serine–threonine protein 2; SYK, spleen tyrosine kinase; IRAK4, IL-1R-related kinase 4; TRAF6, TNF receptor-associated factor 6; TAK1, TGF-β-activated kinase 1; TAB1, 8-adapter-like; TRIF, TIR domain-containing adaptor protein-inducing interferon β; TRAM, TRIF-related adaptor molecule; NOD, nucleotide oligomerization domain; cGAS, cyclic GMP–AMP synthase; cGAMP, 2′3′ cyclic GMP–AMP; STING, stimulator of interferon genes; TBK1, TANK-binding kinase 1; RIG-I, retinoic acid-inducible gene-I; MDA5, melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5; MAVS, mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein; TANK, TRAF family member-associated NFKB activator; SINTBAD, similar to NAP1 TBK1 adaptor; IRF3, interferon regulatory factor 3; CARD9, caspase activation and recruitment domain 9; BCL10, B-cell lymphoma/leukemia 10; MALT1, mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma translocation protein 1; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; AP-1, activator protein 1; NLRP3, NLR family pyrin domain containing 3; ASC, apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing CARD; Arg1, Arginase1; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; COX2, cyclooxygenase-2; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; PD-L1, programmed death-ligand 1; CXCR4, C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4; dsRNA, double-strand RNA; ssRNA, single-strand RNA; IFN-β, interferon-β; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; CXCL9, C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 9; CCL4, C-C motif chemokine ligand 4.