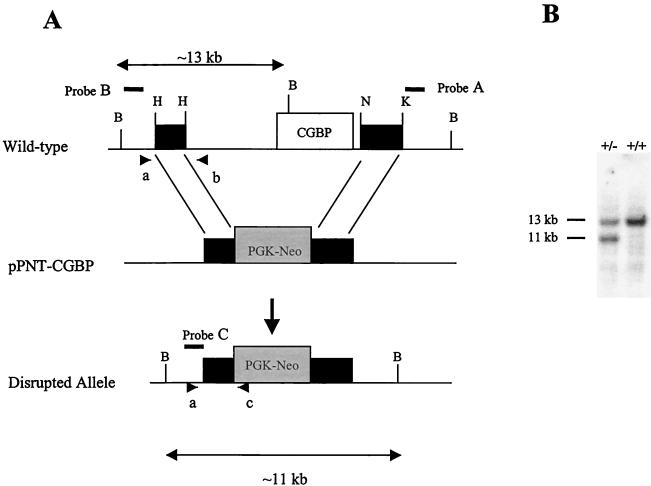
FIG. 1.
Targeted disruption of the murine CGBP gene. (A) Schematic of the disrupted CGBP allele generated by homologous recombination. The open box indicates the CGBP gene, while the black boxes denote the flanking genomic fragments. The gray box denotes PGK-neomycin (Neo). The arrows indicate the sizes of the wild-type (13-kb) and the disrupted (11-kb) BamHI fragment. Probes A to C are designated by solid lines. Oligonucleotide primers a to c used for PCR genotyping are designated by arrowheads. (B) Southern blot analysis was performed on genomic DNAs isolated from wild-type ES cells (+/+) and the ES cell clone (+/−) that contains the disrupted CGBP allele. DNA was digested with BamHI and hybridized with probe B (see above) corresponding to the 5′ flank of the CGBP locus.