Figure 4. Impact of Conditioning Intensity and Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) Measurable Residual Disease Status on Clinical Outcomes.
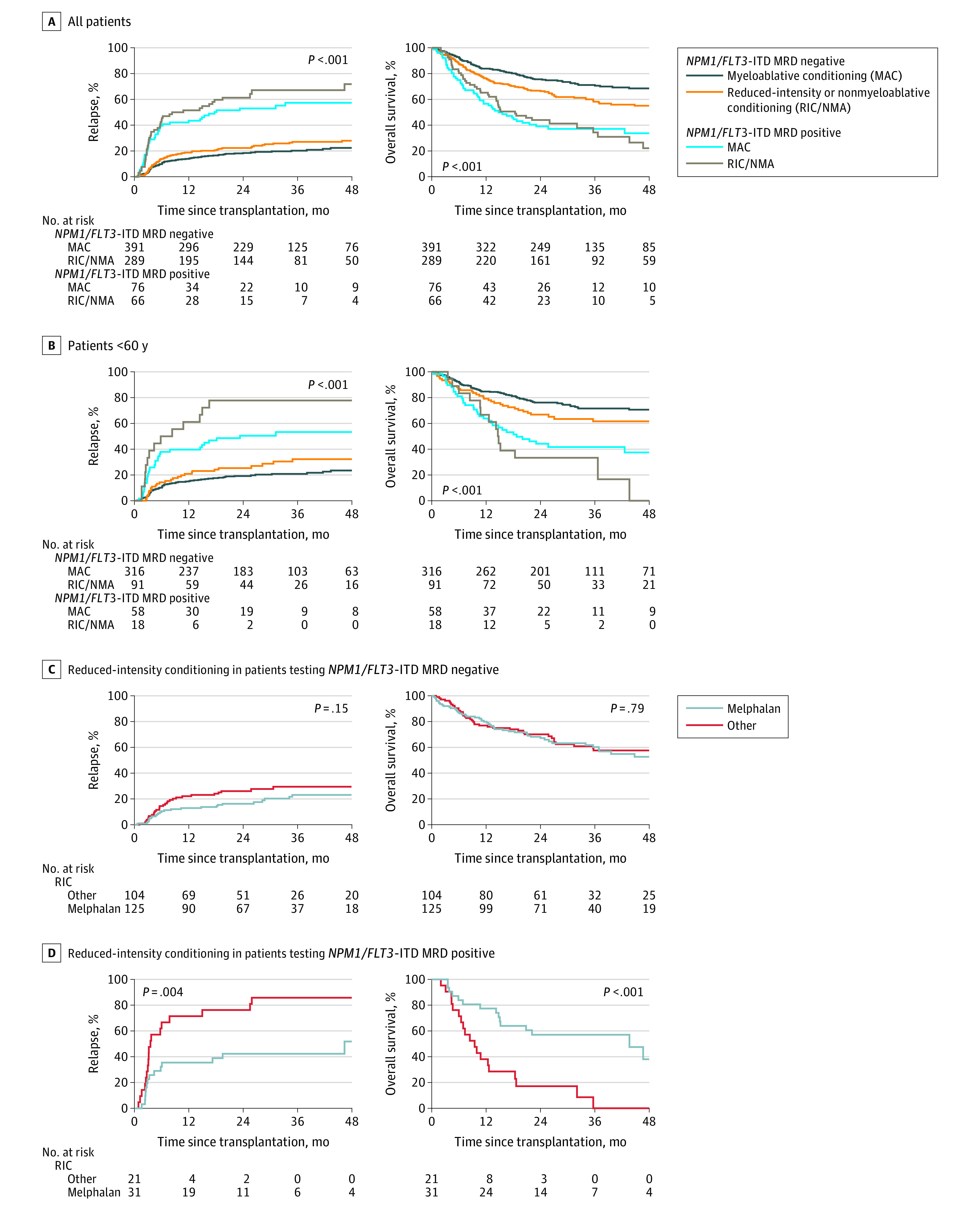
A, Among patients with NPM1 mutated and/or FLT3 internal tandem duplication (FLT3-ITD) acute myeloid leukemia (AML; n = 822), differences in relapse rates and overall survival were identified between subgroups defined by conditioning intensity and NGS-based measurable residual disease (MRD) status.
B, In patients with NPM1 mutated and/or FLT3-ITD AML younger than 60 years (n = 483), MAC regimens resulted in significantly decreased rates of relapse (P = .04) in the MRD-positive group.
C and D, In patients with NPM1 mutated and/or FLT3-ITD AML receiving RIC (n = 281), melphalan conditioning was associated with significantly decreased relapse rates and increased overall survival in the MRD-positive group but not in the MRD-negative group. Median times of observation are listed in eTable 3.
