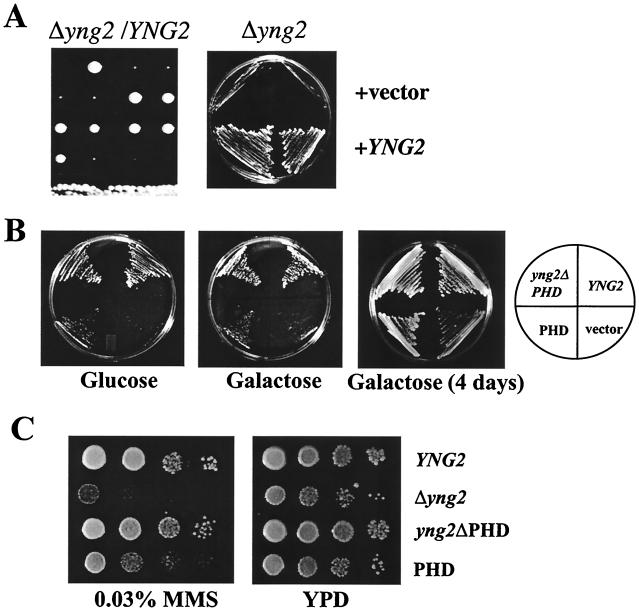
FIG. 3.
Deletion of YNG2 results in slow-growth phenotype and MMS sensitivity that are rescued by the expression of Yng2p deleted of the PHD-finger. (A) The BMA41 diploid strain was disrupted for one copy of YNG2 (QY205) and subjected to sporulation and tetrad dissection. In each case, the spores deleted of YNG2 grew poorly. The deleted haploid strain (QY207: Δyng2) was transformed with low-copy plasmid containing YNG2 (pAN105) or empty vector (−). The wild-type YNG2 gene complements the growth defect phenotype of the disrupted strain. (B) Yng2p deleted for the PHD-finger rescues the growth defect phenotype on glucose and galactose. The Δyng2 strain (QY203) was transformed with plasmid containing wild-type YNG2 (pAN104), YNG2ΔPHD (pYD100), or PHD (pYD101) or an empty vector (−). These strains were plated on minimal medium with either glucose or galactose. After 3 days at 30°C, only the strain expressing Yng2ΔPHD shows normal wild-type growth on either carbon source. Further incubation on galactose shows that all of the strains are able to grow on this medium. (C) The YNG2-null strain is sensitive to MMS. Tenfold serial dilutions of the strains described above were spotted on YPD or YPD + 0.03% MMS plates and incubated at 30°C for 2 days. The strains deleted for YNG2 or expressing only the PHD domain of YNG2 grow poorly on the MMS plate.