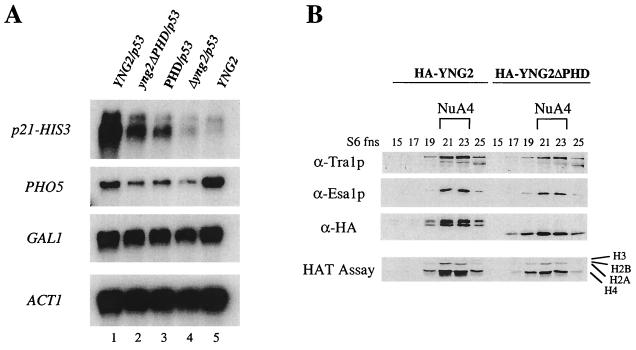
FIG. 7.
Yng2p PHD domain is important for gene-specific transcriptional regulation but is dispensable for NuA4 HAT activity. (A) p53-dependent transcriptional activation is affected in strains deleted of the PHD-finger or expressing only the PHD domain of Yng2p. Δyng2 strains (QY203) containing an episomal copy of wild-type YNG2 (pAN104), yng2ΔPHD (pYD100), or PHD (pYD101) or an empty vector (−) were also transformed with a p53-expressing plasmid (pYD102) and a reporter plasmid encoding His3p under the control of p21 promoter (pSS1). RNA samples were prepared as in Fig. 5, and Northern blots were hybridized with HIS3, PHO5, GAL1, and ACT1 probes. Expression of p21-HIS3 (activated by p53) and PHO5 (basal) is affected by the deletion of Yng2p PHD domain (compare lanes 1 and 2) or its N-terminal domain (compare lanes 1 and 3), while the expression of GAL1 and ACT1 remains unchanged. Equivalent levels of p53 protein between strains were confirmed by Western blot (data not shown). (B) Yng2p PHD-finger domain is not required for NuA4 complex integrity and HAT activity. Protein extracts from deleted strain QY203 expressing HA-Yng2p or HA-Yng2ΔPHD were fractionated over Ni-NTA, MonoQ, and Superose-6 columns. Fractions from the gel filtration were tested for the presence of NuA4 components by Western blot assayed for HAT activity on oligonucleosomes. Deletion of the Yng2p PHD domain does not affect the abundance, integrity, or activity of NuA4.