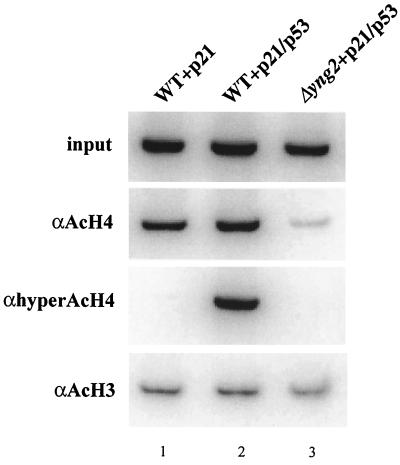
FIG. 8.
Yng2-dependent specific targeting by p53 of histone H4 acetylation to the p21-HIS3 promoter. The Δyng2 strain (QY203) containing an episomal YNG2 gene (pAN104) or an empty vector and the reporter plasmid carrying the p21-HIS3 transcription unit (pSS1) was transformed or not with the p53-expressing plasmid (pYD102). Cultures were grown in minimal medium supplemented with the corresponding auxotrophies to an OD of 1 and then fixed with formaldehyde. The chromatin of each strain was extracted, sonicated, and immunoprecipitated with antiacetylated histone H4, antihyperacetylated histone H4, and antiacetylated histone H3 antibodies as indicated. Input (upper panel) and bound (lower three panels) fractions were assayed for the presence of p21-HIS3 promoter region by PCR amplification (in a ratio of 1:100 for input versus bound). Reactions were analyzed on a 1× TBE–6% polyacrylamide gel. An enhanced level of histone H4 acetylation at the p21-HIS3 promoter is observed in the strain expressing both Yng2p and p53 (compare lanes 1 and 2 for antiacetylated H4 and antihyperacetylated histone H4), while H3 acetylation levels remained constant for all strains. The absence of Yng2p caused a dramatic decrease of H4 acetylation (compare lanes 2 and 3) even below the level present in absence of p53 (compare lanes 1 and 3). These results were reproduced with a different chromatin preparation.