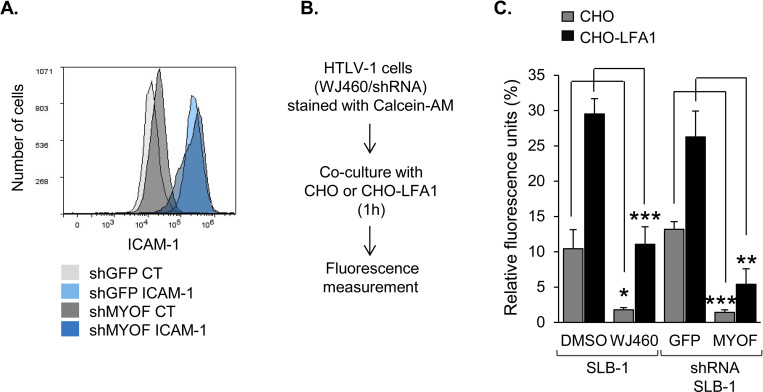
Fig 8. MyoF enhances HTLV-1-infected T-cell adhesion without affecting cell surface abundance of ICAM-1.
(A) Knockdown of MyoF expression does not affect the level of ICAM-1 at the cell-surface. SLB-1 cells stably expressing an shRNA targeting GFP (negative control) or MYOF mRNA were labeled with an antibody against ICAM-1 followed by a FITC-conjugated secondary antibody, fixed and analyzed by flow cytometry. Histograms show relative cell surface labeling as follows: secondary antibody alone- (CT) and ICAM-1-labeled shGFP cells, light gray and light blue, respectively; secondary antibody alone- (CT) and ICAM-1-labeled shMYOF cells, dark gray and dark blue, respectively. (B) Knockdown or inhibition of MyoF reduces adhesion to CHO cells independent of LFA-1 expression. The flow diagram shows the co-culture/adhesion assay procedure using CHO or CHO-LFA-1 adherent cells. (C) Adhesion assays of HTLV-1 infected cells stably expressing shGFP or shMyoF to adherent cells. The graph shows binding of SLB-1 cells pretreated with DMSO or 1 μM WJ460, or SLB-1 cells stably expressing an shRNA targeting GFP (negative control) or MYOF mRNA, to CHO (grey) or CHO-LFA1 (black) cells. Values are the average of three replicates from one experiment and representative of three independent experiments; * p<0.05, ** p<0.01, *** p<0.001.