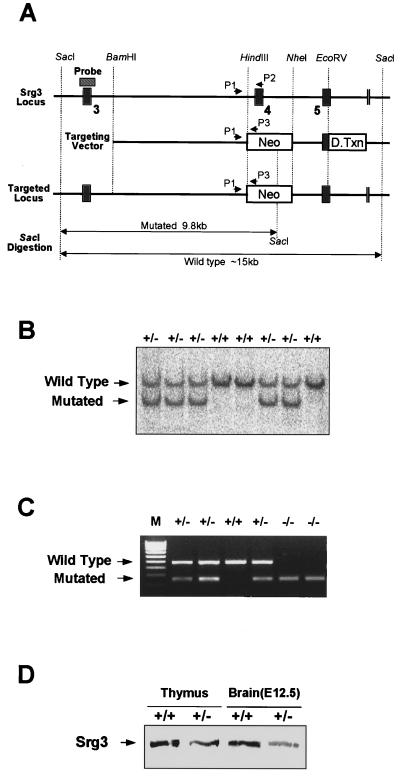
FIG. 3.
Targeting of the Srg3 gene. (A) Schematic diagram of the Srg3 locus and targeting vector and predicted structure of targeted Srg3 allele. Restriction enzyme sites and three exons (3 to 5; black boxes) are shown. The locations of the 5′ flanking Southern probe (hatched box) and PCR primers (P1 to P3) used in panels B and C are indicated. The targeting construct was designed to replace an exon (exon 4) with a PGK-Neo gene. Neo, neomycin resistance gene; D.Txn, diphtheria toxin gene. (B) Southern blot analysis showing correct targeting of the Srg3 locus. Genomic DNA samples were prepared from tails of the progeny derived from Srg3 heterozygous intercrosses, digested with SacI, and probed as indicated. The resulting 15- and 9.8-kb bands correspond to the wild-type and mutated genotypes, respectively. (C) Three-primer PCR analysis of blastocysts from Srg3 heterozygous intercrosses showing wild-type (450-bp) and mutated (250-bp) alleles. M, 100-bp marker. (D) Western blot analysis of Srg3 and Brg1 expression in the thymus (4 to 6 weeks old) and brain at E12.5 from wild-type littermate and Srg3 heterozygous mice.