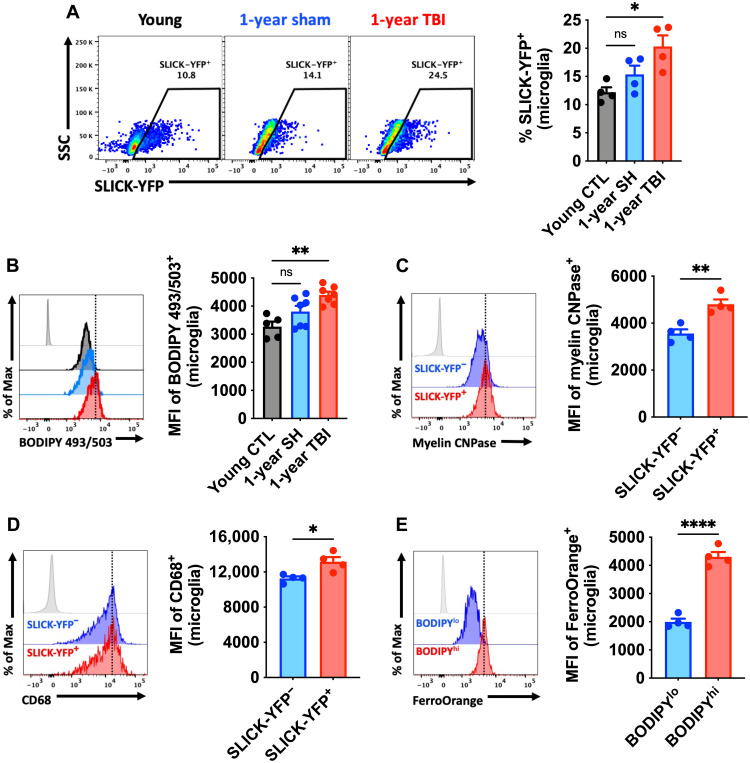
Fig. 9. TBI accelerates development of the AF-related phenotype and chronically increases microglial phagocytosis of apoptotic neurons and myelin.
Microglial phagocytosis of neurons was assessed by ex vivo engulfment of apoptotic cortical neurons isolated from SLICK-YFP transgenic reporter mice. (A) Representative dot plots of microglia expressing YFP at 1 year after TBI. Quantification of phagocytic microglia is shown (right). (B) A representative histogram of BODIPY+ microglia at 1 year after TBI is shown next to the MFI quantification of this neutral lipid marker. (C) A representative histogram shows the relative protein expression of myelin CNPase in YFP− phagocytic and nonphagocytic microglia at 1 year after TBI. (D) A representative histogram shows the relative expression level of the phagocytosis marker CD68 in YFP+ and YFP− microglia. The MFI of CD68+ microglia is quantified. (E) A representative histogram shows the relative level of intracellular iron deposition in subsets of microglia that are low and high in neutral lipid content at 1 year after TBI. N = 4 to 7 per group. FMO controls are shown in light gray, while all other groups are shown with bold outline as color-coded according to the bar graph axis labels. A vertical fiducial line is included for reference. CTL, control; SH, sham; ns, not significant.. Data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc correction for multiple comparisons (A and B) and Student’s t test (C to E) (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ****P < 0.0001).