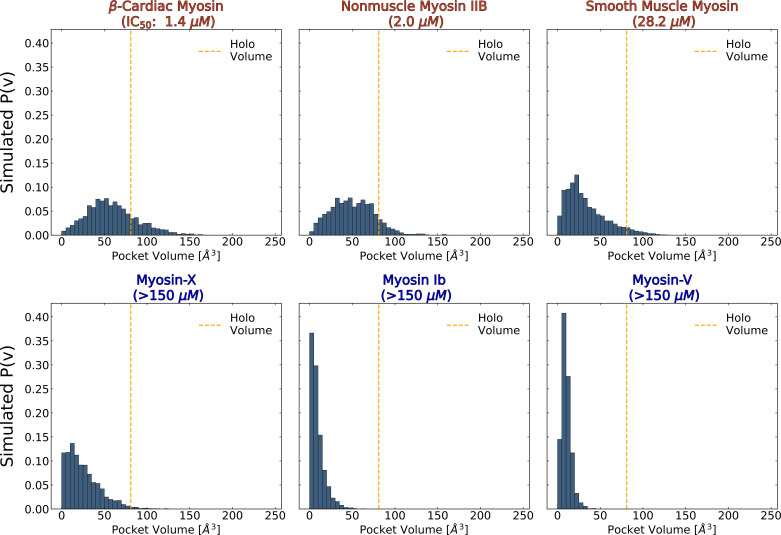
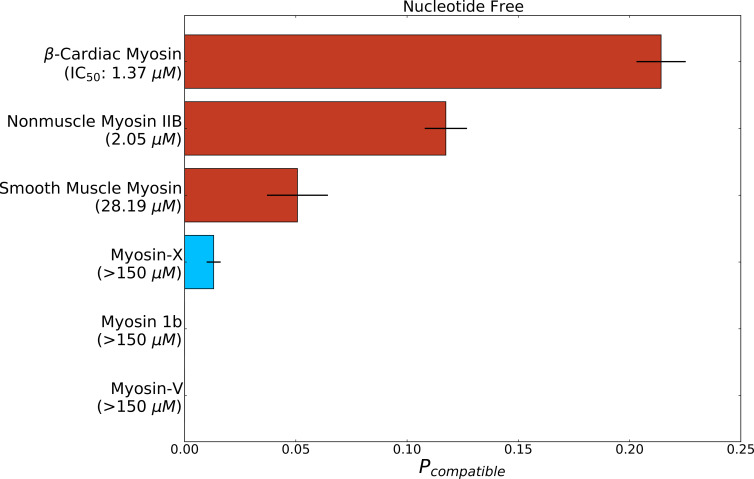
Figure 4. The probability of adopting open pocket conformations is greater among blebbistatin-sensitive isoforms (top row) than insensitive isoforms (bottom row).
MSM-weighted distributions of blebbistatin pocket volumes in simulations of nucleotide-free isolated myosin motor domains show that myosin-IIs (top row) are more likely to exceed the blebbistatin pocket volume of a holo crystal structure (PDB: 1YV3, orange line) than non-class II myosins. Among myosin-IIs, those with lower IC50s (Limouze et al., 2004; Eddinger et al., 2007; Wang et al., 2008; Zhang et al., 2017; Várkuti et al., 2016; Radnai, 2021) have more right-shifted pocket volume distributions. The overall opening probabilities between these isoforms can be visualized in Figure 4—figure supplement 1. Note that reported pocket volumes are smaller than the space available to ligands because of an algorithm choice made to avoid erroneous detection of small pockets (see Materials and methods for details).