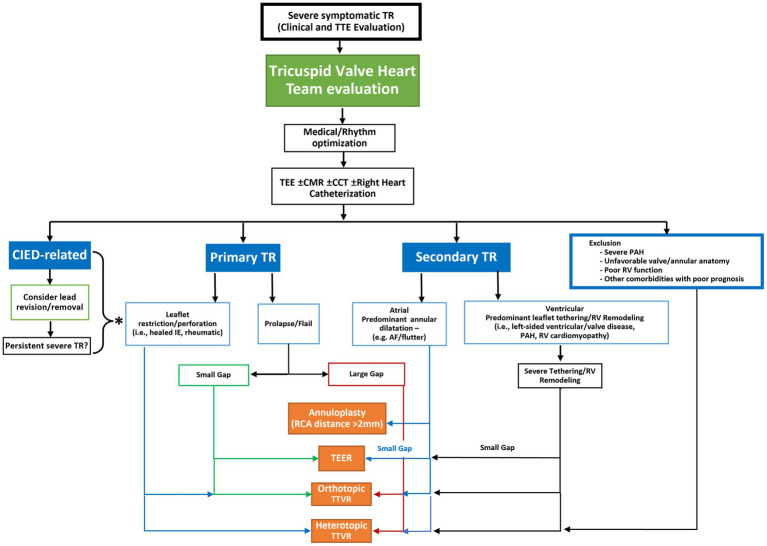
Figure 3.
Proposed anatomic algorithm for the selection of transcatheter tricuspid valve intervention systems. Following a determination of the presence of severe, symptomatic tricuspid regurgitation (TR), the patient should be referred to a heart team with experience in management of TR. Patients should be medically optimized which may entail rhythm management. If TR persists, then a more comprehensive imaging or invasive assessment may be required to determine the etiology and morphology of the disease. Once this is determined the anatomic characteristics of the disease may determine the most appropriate transcatheter therapy. *If severe TR persists after lead removal, or the TR is not caused by the cardiac implantable electronic device (CIED) then the etiology of the TR should be assessed to determine the possible device choices. CCT, cardiac computed tomography; CIED: cardiac implantable electronic device; CMR, cardiac magnetic resonance imaging; IE, infective endocarditis; MDT, multidisciplinary team; PAH, pulmonary arterial hypertension; RCA, right coronary artery; TEE, transesophageal echocardiography; TEER, transcatheter edge-to-edge repair; TR, tricuspid regurgitation; TTVR, transcatheter tricuspid valve replacement.