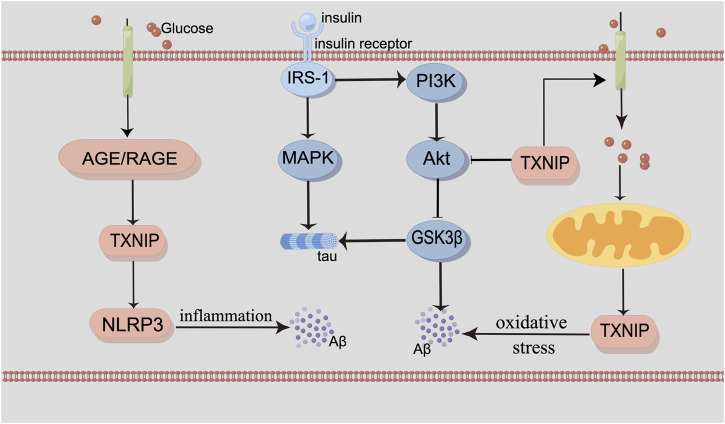
FIGURE 1.
By Figdraw. The interaction of glucose metabolism and the pathogenesis of AD. Insulin binds to the insulin receptor, recruiting the IRS-1 proteins and triggering two signaling cascades, including the MAPK pathway and the PI3K/Akt/GSK3β pathway. Inhibition of PI3K and downregulation of the phosphorylated Akt protein subsequently activate GSK3β. TXNIP is a modulator of glucose metabolism and oxidative stress. It can also be induced by AMPK. RAGE/TXNIP/NLRP3 inflammasome can lead to neuroinflammation. Abnormal mitochondrial function can interact with glucose metabolism. MAPK signaling participates in the phosphorylation of tau. And the activation of GSK3β can also contribute to Aβ production and tau phosphorylation, as well as neuroinflammation and oxidative stress.