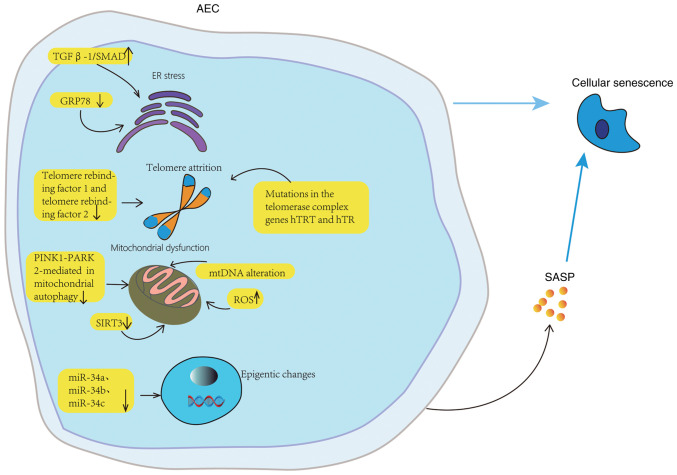
Figure 2.
Aging mechanism of AECs. The senescence and apoptosis of AECs may be related to ER stress, autophagy, telomere damage, mitochondrial dysfunction, and epigenetic changes. In aging lungs, AECs are particularly sensitive to ER stress. GRP78 knockout decreases ER stress, injury, aging and differentiation, and TGF-β 1/Abnormal activation of SMAD signaling. Normal aging is accompanied by telomere shortening, while mutations in hTRT and hTR of telomerase complex gene accelerate telomere shortening and lead to replicative aging of AECs. In the pathogenesis of IPF, mitochondrial dysfunction involves the imbalance of mitochondrial ROS level, the change of mitochondrial DNA, the downregulation of mitochondrial autophagy mediated by PINK1-PARK2, and the downregulation of SIRT3 expression. The high expression of miR-34a, miR-34b and miR-34c can lead to the aging of AECs. AEC, alveolar epithelial cell; GRP78, glucose regulatory protein 78; hTRT, human telomerase reverse transcriptase; hTR, human telomerase RNA; mtDNA, mitochondrial DNA; PINK1, PTEN-induced putative kinase 1; PARK2, parkin RBR E3 ubiquitin protein ligase; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SASP, senescence-associated secretion phenotype; SIRT3, NAD-dependent deacetylase sirtuin-3; miR, microRNA.