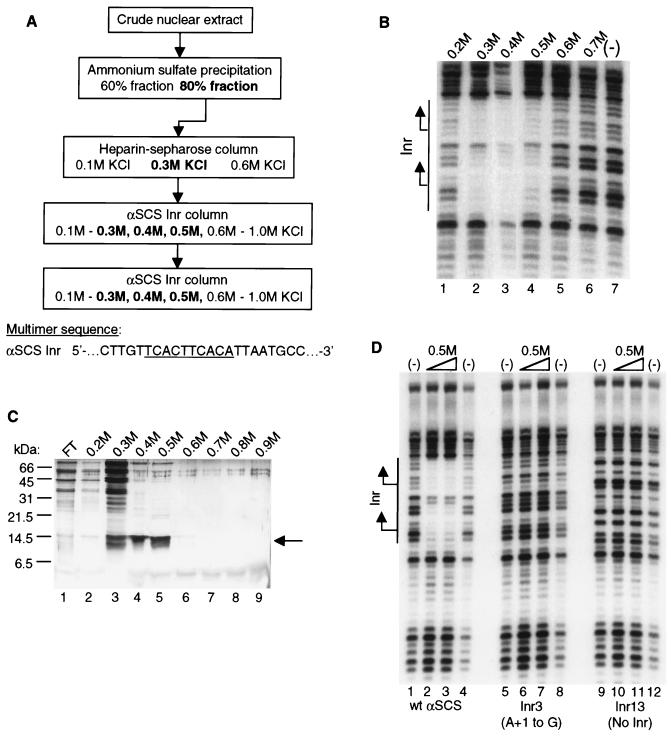
FIG. 2.
Purification of the initiator-specific binding activity. (A) Purification scheme for Inr-specific binding activity from T. vaginalis nuclear extracts. Column elutions were performed by using the indicated concentrations of KCl. The fractions that contained binding activity, as assessed by DNase I footprinting assays, are shown in boldface. The sequence of the αSCS Inr attached as a multimer to the DNA affinity columns is shown with the Inr motif underlined. (B) DNase I footprinting assay with fractions from the final αSCS Inr column. Footprinting reactions were performed with either the 0.2 to 0.7 M KCl αSCS Inr column fractions (lanes 1 to 6, respectively) or no protein (lane 7) and the wild-type αSCS Inr probe. No binding activity was detected in the flowthrough fraction (not shown). The DNA sequence of the Inr region of the probe in shown in Fig. 1. The location of the Inr element is shown with the two transcription start sites indicated by arrows. (C) Protein profile of fractions from the final αSCS Inr column. Protein from each fraction was precipitated with 25% TCA and separated on a 17.5% Tris-glycine SDS-PAGE gel, followed by silver staining. Lane 1, flowthrough fraction; lanes 2 to 9, 0.2 to 0.9 M KCl eluates from the αSCS Inr column. Positions of the molecular mass markers are indicated to the left. The 14.5-kDa protein band enriched in the 0.3 to 0.5 M KCl fractions is indicated by the arrow. (D) DNase I footprinting assay with the 0.5 M KCl eluate from the final αSCS Inr column. Footprinting reactions were performed with either no protein (lanes 1, 4, 5, 8, 9, and 12) or 5 μl (lanes 2, 6, and 10) or 10 μl (lanes 3, 7, and 11) of the 0.5 M KCl Inr column eluate and the wild-type αSCS Inr (lanes 1 to 4), Inr3 (lanes 5 to 8), or Inr13 (lanes 9 to 12) probes. The DNA sequence of the Inr region of the probes is shown in Fig. 1. The location of the Inr element is shown at the left with the two transcription start sites indicated by arrows.