FIG. 6.
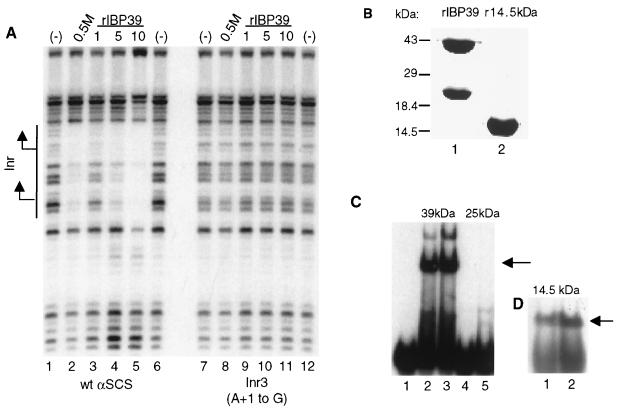
IBP39 specifically binds the initiator. (A) DNase I footprinting assays were performed with either the wild-type αSCS Inr (lanes 1 to 6) or the Inr3 (lanes 7 to 12) probes and either no protein (lanes 1, 6, 7, and 12), 5 μl of the 0.5 M KCl final Inr column fraction (lanes 2 and 8), 1 ng of recombinant IBP39 (lanes 3, 9), 5 ng of recombinant IBP39 (lanes 4 and 10), or 10 ng of recombinant IBP39 (lanes 5, 11). The location of the Inr element is shown with the two transcription start sites indicated by arrows. (B) Recombinant IBP39 (lane 1) and a 14.5-kDa N-terminal peptide corresponding to amino acids 1 to 125 of IBP39 (lane 2) were expressed in E. coli and separated on an SDS-PAGE gel. (C) Mobility shift assay using the −15/+15 αSCS Inr probe and the 39- and 25-kDa proteins recovered from the gel after the denaturation-renaturation protocol. Lane 1, no protein; lanes 2 and 3, either 1 or 5 μl, respectively, of the 39-kDa protein; lanes 4 and 5, either 1 or 5 μl, respectively, of the 25-kDa protein. (D) Mobility shift assay using the −15 or +15 αSCS Inr probe and 5 ng (lane 1) or 10 ng (lane 2) of the 14.5-kDa recombinant protein. The Inr-specific binding activities are indicated by the arrows.