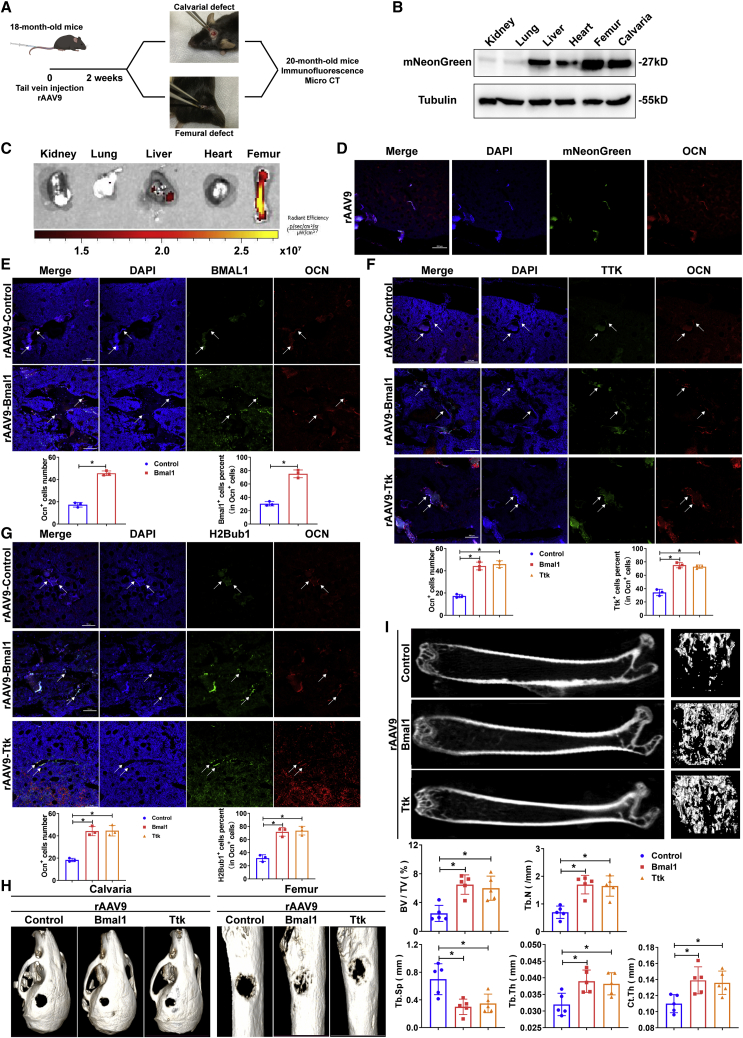
Figure 7.
Bone-targeted Bmal1 or Ttk rescue-treated senile osteoporosis
(A) Diagram showing the workflow of rAAV9 injection in 18-month-old mice with calvarial and femoral defects and bone section analysis. (B) Immunoblot analysis showing mNeonGreen expression in different organs of the mice injected with rAAV9. (C) Fluorescence images of different organs of mice injected with rAAV9. (D) Immunofluorescence staining (scale bar, 100 μm) showing mNeonGreen-expressing osteoblasts in the femurs of the mice injected with rAAV9. (E) Immunofluorescence staining (scale bar, 100 μm) showing Bmal1 expression in the Ocn+ osteoblast lineage in the mice injected with rAAV9-control or rAAV9-Bmal1 (white arrows). (F) Immunofluorescence staining (scale bar, 100 μm) showing Ttk expression in the Ocn+ osteoblast lineage in the mice injected with rAAV9-control, rAAV9-Bmal1, or rAAV9-Ttk (white arrows). (G) Immunofluorescence staining (scale bar, 100 μm) showing H2Bub1 levels in the Ocn+ osteoblast lineage in the mice injected with rAAV9-control, rAAV9-Bmal1, or rAAV9-Ttk (white arrows). Data are presented as mean ± SD; n = 3; ∗p < 0.05. (H) Micro-CT analysis comparing the healing rates of calvarial and femoral defects in the mice injected with rAAV9-control, rAAV9-Bmal1, or rAAV9-Ttk. (I) Representative micro-CT images showing the trabecular bone of mice with senile osteoporosis injected with rAAV9-control, rAAV9-Bmal1, or rAAV9-Ttk. Bone morphometric analysis, including the analysis of BV/TV, Tb.Th, Tb.N, Tb.Sp, and Ct.Th., was performed. Data are presented as mean ± SD; n = 5; ∗p < 0.05.