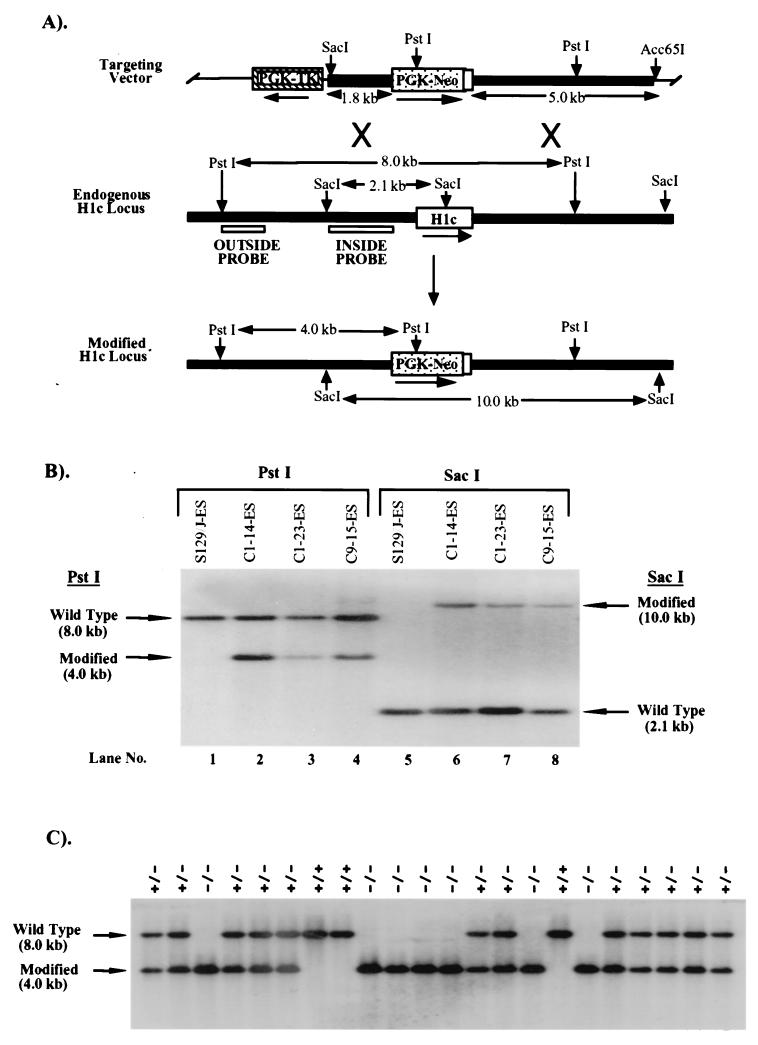
FIG. 1.
Targeted disruption of the H1c gene in mouse ES cells and mice. (A) Homologous-recombination strategy in ES cells. The H1c targeting vector (top) was constructed by removing a 566-bp ApaI/MscI segment from a 6.4-kb EcoRI genomic fragment cloned in pGEM-3Z (Promega), containing the H1c coding region (open box), and inserting by blunt-end ligation a 1.8-kb ApaI/HindIII fragment (stippled box) from PGK-NEO. The 7.2-kb H1c/PGK-NEO insert was subsequently released by SalI digestion and inserted into the XhoI site of pPGK-TK (19). To increase the length of homology within the short arm (5′ of PGK-NEO), the 0.8-kb ClaI-XhoI short-arm fragment was removed and replaced with a ClaI-XhoI 1.8-kb homologous H1c 5′ region fragment from H1c plasmid subclone HS7 (22). The transcriptional orientations of the genes are indicated by arrows. A homologous recombination event (X's) between the targeting vector and the endogenous H1c locus (middle) results in production of a modified H1c locus (bottom) in which a segment from 58 bp 5′ of the translation initiation codon to codon 170 was replaced with PGK-NEO. (B) Identification of ES cell clones containing the modified H1c allele. After an initial screening of pools of two ES cell clones, ES cell DNA (10 μg) from individual clones was digested with PstI (lanes 1 to 4) and Southern blot hybridized with the outside probe (A). Correct targeting was confirmed (lanes 5 to 8) by SacI digestion of ES cell DNA and blot hybridization with the inside probe (A). Results obtained with DNA from untransfected ES cells are shown in lanes 1 and 5. The expected positions of the hybridizing fragments from the unmodified (wild-type) and modified H1c loci and their respective sizes are indicated. (C) Genotype analysis of offspring from parents heterozygous for the modified H1c allele. Siblings that were heterozygous for the modified H1c allele were bred, and 15 μg of tail DNA from offspring was digested with PstI and blot hybridized with the inside probe (Fig. 1A). The deduced genotype of each animal is indicated above each lane. The expected positions of the hybridizing fragment from the wild-type and modified loci and their corresponding sizes are indicated.