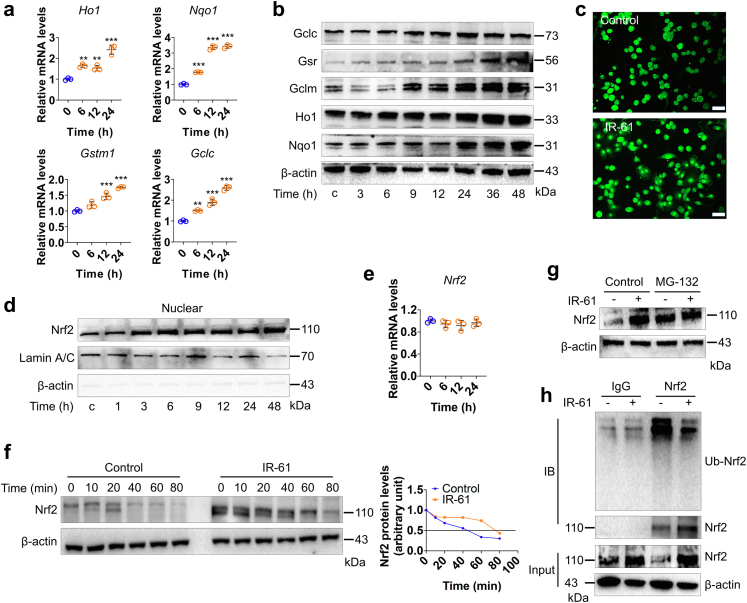
Fig. 4.
IR-61 activates Nrf2 by preventing its ubiquitin-proteasome degradation. (a) The mRNA levels of Nrf2 target genes were measured at various time points after treatment with 10 μM IR-61 (Ho1: 0 vs 6 h p = 0.0031, 0 vs 12 h p = 0.0099, 0 vs 24 h p < 0.0001; Nqo1: 0 vs 6 h p < 0.0001, 0 vs 12 h p < 0.0001, 0 vs 24 h p < 0.0001; Gstm1: 0 vs 6 h p = 0.0947, 0 vs 12 h p = 0.0004, 0 vs 24 h p < 0.0001; Gclc: 0 vs 6 h p = 0.0021, 0 vs 12 h p < 0.0001, 0 vs 24 h p < 0.0001; n = 3 per group). (b) The levels of proteins downstream of Nrf2 were measured after treatment with 10 μM IR-61. β-actin was used as the loading control. (c) Immunofluorescence staining of Nrf2 in PMs treated with 10 μM IR-61 for 24 h. Representative images are shown (bars represent 25 μm; n = 3 per group). (d) Protein level of Nrf2 in nucleus was detected at various time points after treatment with 10 μM IR-61. Lamin and β-actin served as markers for nuclear and cytosolic proteins, respectively. (e) The mRNA levels of Nrf2 were measured at various time points after treatment with 10 μM IR-61 (Nrf2: 0 vs 6 h p > 0.9999, 0 vs 12 h p = 0.5833, 0 vs 24 h p > 0.9999; n = 3 per group). (f) Immunoblots for Nrf2 in whole cell lysates from control and IR-61-treated PMs in the presence of 100 mg mL−1 CHX at the various time points (left). Nrf2 band intensity was quantified by ImageJ and Nrf2 levels in the untreated cells were normalized to 1 (right). (g) Immunoblots for Nrf2 in whole cell lysates from control and IR-61-treated PMs in the presence or absence of proteasome inhibitor MG132. (h) The Ub-Nrf2 was measured by co-immunoprecipitation (co-IP) of Nrf2 using a subsequent western blot assay with anti-ubiquitin antibody in control or IR-61-treated macrophages. Results are presented as the mean ± SD (∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗p < 0.001; one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-hoc test).