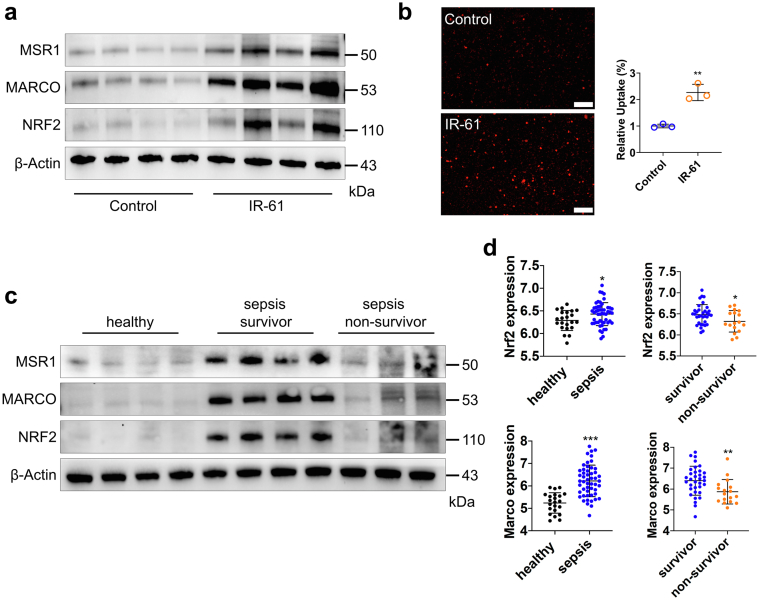
Fig. 8.
Nrf2 is activated by IR-61 in human macrophages and may associate with sepsis outcomes. (a) NRF2, MARCO, and MSR1 protein levels in human macrophages treated with IR-61 for 24 h. β-actin was used as the loading control (n = 4 healthy humans per group). (b) Human macrophages were treated with 10 μM IR-61 for 24 h, and then incubated with pHrodo-labelled E. coli for another 1 h. Uptake was measured by fluorescent microscopy (Control vs IR-61: p = 0.0022; n = 3 plates of human macrophages per group and random observation of 3 visual fields per plate; bars represent 100 μm). (c) NRF2, MARCO, and MSR1 protein levels in circulating CD14+ monocytes isolated from the blood (n = 4 for healthy controls, n = 4 for sepsis survivors, and n = 3 for sepsis non-survivors). (d)Nrf2 and Marco mRNA levels in the peripheral blood (healthy vs sepsis: p = 0.0273 (Nrf2), p < 0.0001 (Marco), survivor vs non-survivor: p = 0.0321 (Nrf2), p = 0.0097 (Marco); n = 22 for healthy controls, n = 51 for sepsis patients, n = 34 for sepsis survivors, and n = 17 for sepsis non-survivors). Data were obtained from GSE95233 dataset. Results are presented as the mean ± SD (∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗p < 0.001; two-sided Student's t-test).