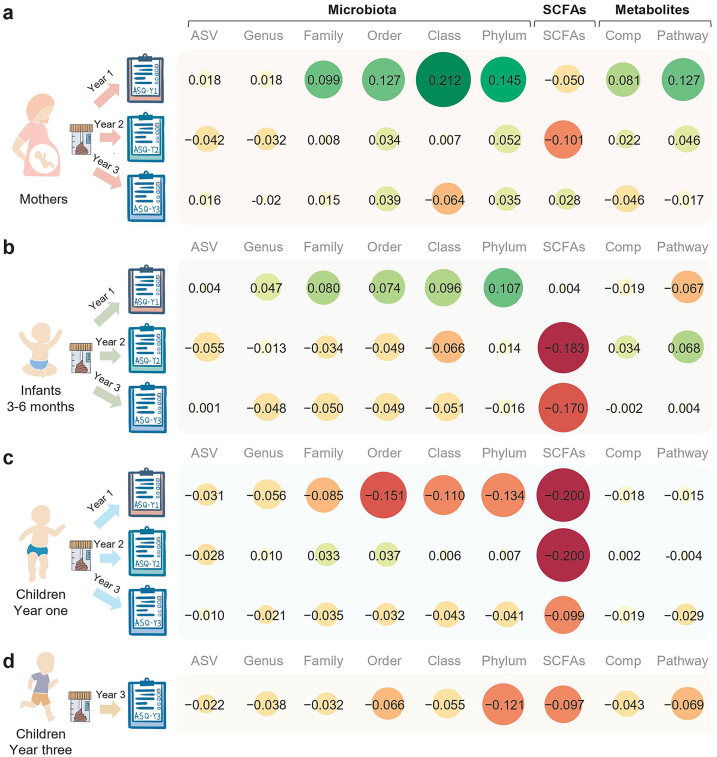
Fig. 3.
Average discriminating power (Q2) of the gut microbiome for the ASQ in five domains. (a) The discriminating power of the maternal prenatal gut microbiome for child neurodevelopment. (b) The discriminating power of the infant gut microbiome in early life (months 3–6) for child neurodevelopment. (c) The discriminating power of the child gut microbiome at year one for child neurodevelopment. (d) The discriminating power of the child gut microbiome at year three for child neurodevelopment at the same time point. Red pies indicate negative Q2 and green pies indicate positive Q2. The number in each pie chart is the average Q2 of communication skills, fine motor skills, gross motor skills, personal social skills, and problem-solving skills. The higher Q2 (positive) indicates a higher discriminant accuracy for ASQ, while negative Q2 indicates poor discriminant accuracy or overfitting of the multinomial regression models for ASQ measures. The value less than −0.2 will be trimmed to −0.2 for visualization, and comp is short for compound (metabolite).