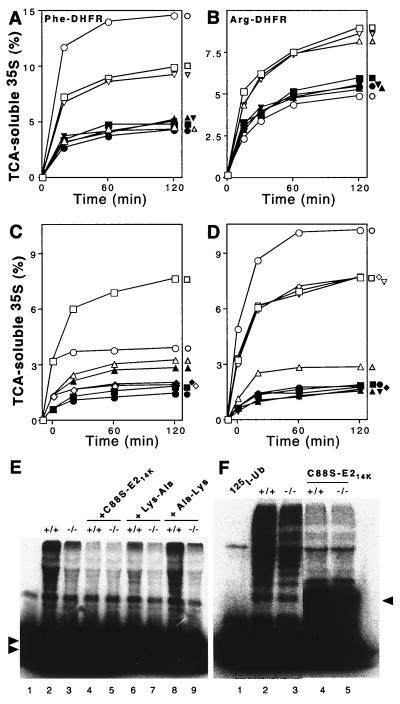
FIG. 6.
Extracts from skeletal muscle of UBR1−/− mice lack the N-end rule pathway. Degradation of 35S-labeled, purified Ub-X-DHFR test proteins in extracts from skeletal muscle of +/+ and UBR1−/− littermates (strain 129 background) was monitored by measuring TCA-soluble 35S (see Materials and Methods). Open and closed symbols denote, respectively, the data with +/+ and UBR1−/− extracts. (A) Degradation of Phe-DHFR, a type 2 N-end rule substrate. □ and ▪, no dipeptide inhibitor; ○ and ●, Lys-Ala; ▵ and ▴, Phe-Ala; ▿ and ▾, Ala-Lys (control dipeptide). (B) Degradation of Arg-DHFR, a type 1 substrate. □ and ▪, no dipeptide inhibitor; ○ and ●, Lys-Ala; ▵ and ▴, Phe-Ala; ▿ and ▾, Ala-Lys. (C and D) The N-end rule-specific degradation of Phe-DHFR is ATP-dependent. Reaction mixtures were incubated at 37°C for 10 min without ATP followed by assays either in the absence or the presence of added ATP. (Time zero corresponds to the end of 10-min preincubation in the absence of ATP to allow deubiquitylation of Ub-X-DHFRs.) (C) Degradation of Phe-DHFR in the presence (□ and ▪) or absence (○ and ●) of added ATP, and of Met-DHFR (not an N-end substrate) in the presence (▵ and ▴) or absence (⋄ and ♦) of ATP. (D) Effect of Lys-Ala, a type 1 dipeptide inhibitor, on the ATP-dependent degradation of Phe-DHFR, a type 2 N-end rule substrate. □ and ▪, no inhibitor; ○ and ●, Lys-Ala; ▵ and ▴, Phe-Ala; ⋄ and ♦, Ala-Lys; ▿ and ▾, Ala-Phe. (E) Conjugation of unlabeled Ub to 125I-α-lactalbumin (a type 1 N-end rule substrate) is decreased in the extract from UBR1−/− muscle. Some of the samples contained either the dominant-negative E214K(C88S) mutant protein (at 2 μM), 2 mM Lys-Ala, or 2 mM Ala-Lys. Double arrowheads on the left indicate the excess of unconjugated 125I-α-lactalbumin. Lane 1, 125I-α-lactalbumin alone. (F) Conjugation of 125I-Ub to endogenous proteins is marginally decreased in a UBR1−/− muscle extract compared to that in the wild-type extract. Fraction II (see Materials and Methods) of muscle extracts from +/+ and UBR1−/− mice was supplemented with AMP-PNP, and the formation of 125I-Ub-protein con- jugates was assayed by SDS-PAGE in the ab- sence (lanes 2 and 3) or presence (lanes 4 and 5) of 2 μM E214K(C88S). Arrowhead on the right indicates the position of 125I-Ub-E214K(C88S) conjugate. Lane 1, 125I-Ub alone. The results shown in panels A through D are typical of those obtained in at least five independent experiments, using three independently produced muscle extract preparations, and two independent EF cell extracts (see Fig. 7), in combination with two independent preparations of [35S]Ub-X-DHFR.