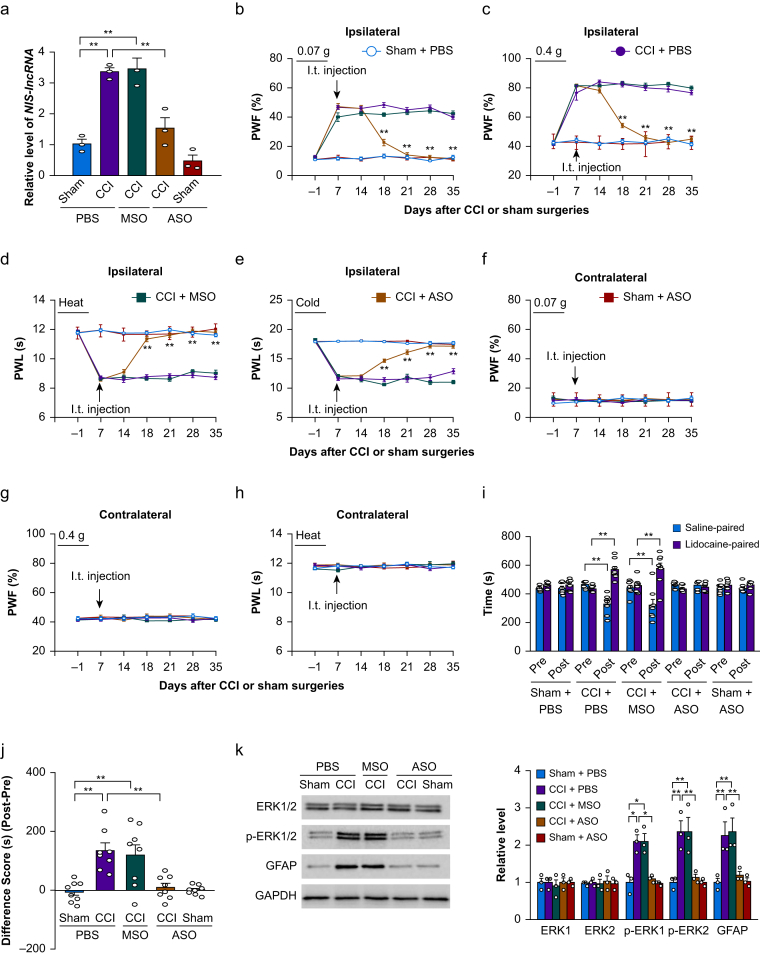
Fig 1.
Intrathecal (i.t.) administration of nerve injury-specific long non-coding RNA (NIS-lncRNA) antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) blocked the chronic constriction injury (CCI)-induced NIS-lncRNA increase in injured dorsal root ganglion (DRG) and nociceptive hypersensitivity. ASOs (100 μg), missense oligonucleotides (MSOs; 100 μg) or phosphate buffered saline (PBS) 0.01 M was injected intrathecally on day 7 after CCI or sham surgery. (a) Level of NIS-lncRNA in the ipsilateral lumbar 3/4 DRGs on day 35 after CCI or sham surgery in the mice with treatments as indicated. n=3 repeats (6 mice)/group. ∗∗P<0.01, by two-way analysis of variance (anova) followed by post hoc Tukey test. (b–h) Effect of i.t. administration of NIS-lncRNA ASOs, MSOs, or PBS on paw withdrawal frequency (PWF) to 0.07 g (b and f) and 0.4 g (c and g) von Frey filament stimuli and paw withdrawal latency (PWL) to heat (d and h) and cold (e) stimuli on the ipsilateral (b–e) and contralateral (f–h) sides on days as indicated after CCI or sham surgery. n=12 mice/group. ∗∗P<0.01 vs the PBS-treated CCI group at the corresponding days, by three-way anova with repeated measures followed by post hoc Tukey test. (i and j) Effect of i.t. administration of NIS-lncRNA ASOs, MSOs, or PBS on ongoing nociceptive responses as assessed by the conditioned place preference paradigm on day 28 post-CCI or sham surgery. Post, post-conditioning; Pre, preconditioning. n=8 mice/group. ∗∗P<0.01, by three-way anova with repeated measures followed by post hoc Tukey test (i) or two-way anova followed by post hoc Tukey test (j). (k) Effect of i.t. administration of NIS-lncRNA ASOs, MSOs, or PBS on the levels of phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 and 2 (p-ERK1/2), ERK1/2, and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) in the ipsilateral lumbar 3/4 dorsal horn 35 days after CCI or sham surgery. GAPDH (glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase) was used as a loading control. n=3 repeats (6 mice)/group. ∗P<0.05, ∗∗P<0.01, by two-way anova followed by post hoc Tukey test.