Fig. 1.
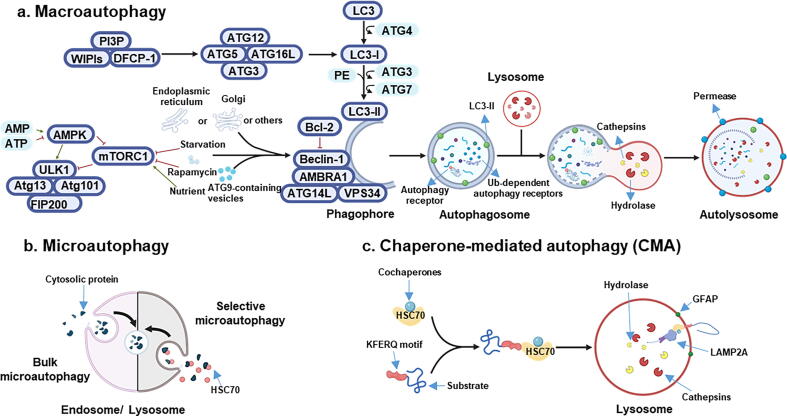
Molecular machinery of autophagy. a) AMPK is the major energy-sensing kinase in the cell and responds to intracellular AMP/ATP ratio. A low energy state, associated with high AMP and a low ATP level, activates AMPK which in turn phosphorylates the TSC1/TSC2 complex by inhibiting the activity of mTORC1. In contrast, signals such as growth factors and nutrient abundance lead to inhibition of autophagy through mTORC1, which phosphorylates and associates with the induction complex ULK1/2-ATG13-ATG101-FIP2000 by preventing autophagic cascade. Under rapamycin treatment and starvation, mTORC1 dissociates from the induction complex, resulting in autophagy induction. This triggers phosphorylation of components of the class III PI3K (PI3KC3) complex I (including class III PI3K, VSP34, Beclin-1, ATG14, AMBRA1) which triggers nucleation of the phagophore. The source of membrane includes mitochondria, plasma membrane, Golgi apparatus, endoplasmic reticulum and ATG9-containg vesicles. The anti-apoptotic protein Bcl2 binds Beclin-1 and prevents its interaction with PI3KC3 and, in turn, autophagy. The PI3KC3 complex activates and recruits phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate (PI3P) and its effector proteins WIPIs and DFCP1.This complex binds the ATG12-ATG5-ATG16L1 complex that promotes cleavage of LC3 by ATG4 to form LC3-I and its lipidated form with phosphatidylethanolamine (PE), which is integrated in the pre-autophagosomal and autophagosomal membrane, where LC3-II interacts with cargo receptors containing LC3-interacting motif (LIR). Finally, the mature autophagosome fuses with a lysosome, where acidic hydrolases and proteases, such as cathepsins, degrade the autophagic cargo. Lysosomal activity is mainly regulated by TFEB, whose nuclear translocation is promoted by a lower phosphorylation induced by AMPK activation. After degradation, component parts of the autophagic cargo are exported back into the cytoplasm through lysosomal permeases for use by the cell in biosynthetic processes or to produce energy. b) Microautophagy involves the direct uptake of the cargo through invagination of the lysosomal or late endosomal membrane. c) In chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA), HSC70 together with co-chaperones binds KFERQ pentapeptide motif. Then, LAMP2A, a lysosomal membrane receptor, drives the degradation. The activity of this receptor is modulated by the glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP).