Fig. 3. Cocaine abstinence and i.c.v. gp120 exposure alter neuroimmune function in the NAc core.
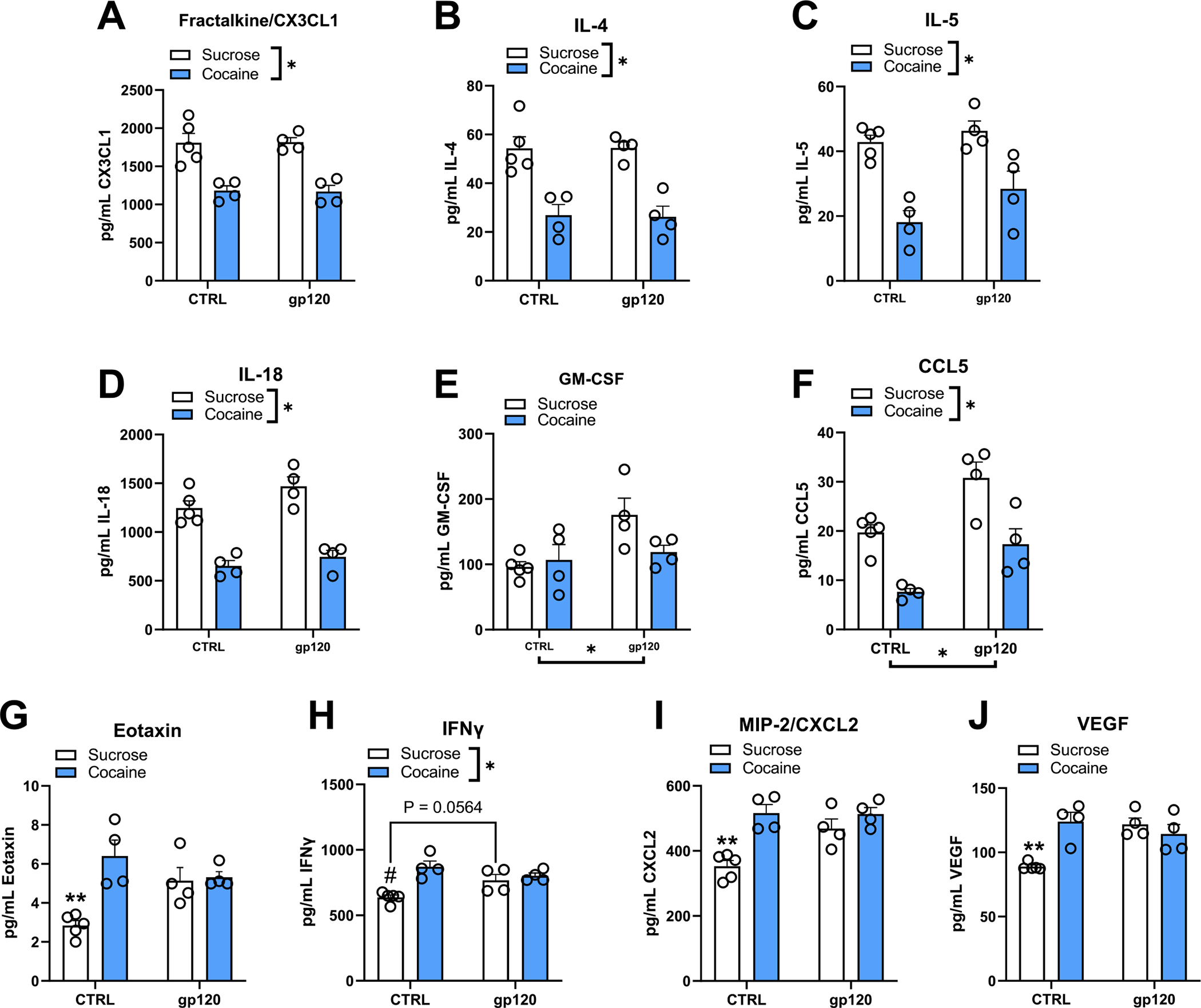
(A-J) Two-way ANOVAs revealed a significant main effect of early cocaine abstinence for fractalkine/CX3CL1, IL-4, IL-5, IL-18, and CCL5 where cocaine abstinence decreased the expression of these targets regardless of gp120. Conversely, a significant main effect of gp120 exposure was detected for CCL5 and GM-CSF, where gp120 increased the expression of these targets regardless of abstinence condition, although this is likely driven by the sucrose + gp120 group for GM-CSF. Significant interactions were detected between early cocaine abstinence and subchronic exposure to gp120 for eotaxin, IFNγ, MIP-2/CXCL2, and VEGF compared to unexposed, sucrose-abstinent rats (i.e., sucrose + CTRL group). Expression of these targets was increased to a similar degree due to cocaine abstinence, gp120 exposure, or their combination relative to sucrose controls. Overall, no additive or synergistic effects of combined gp120 and early cocaine abstinence were observed. ∗p < 0.05, ANOVA main effect (brackets indicate significant effect of the manipulation); ∗∗p < 0.05 relative to all other treatment groups; #p < 0.05 relative to CTRL-cocaine and gp120-cocaine groups. Error bars = SEM; n = 4–5/group.
