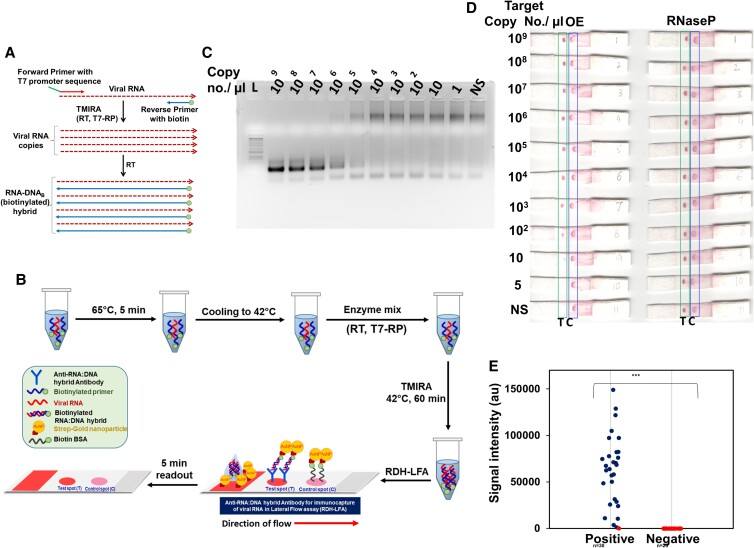
Fig. 4.
TMIRA improves sensitivity of RDH-LFA method. (A) Schematic representation of TMIRA, leading to amplification of target RNA in presence of forward primer having 5'-overhang containing T7-RP promoter sequence and reverse primer tagged with biotin at 5'-end giving rise to biotin-tagged-RDH (for details see Figure S3). (B) Experimental workflow of RDH-LFA coupled with TMIRA: Target RNA, specific primers and buffers are incubated at 65°C for 5 min for denaturation followed by annealing at 42°C. The thermostable enzymes mix (RT and T7-RP) along with NTPs are added to the reaction tube and incubated at 42°C for 60 min for a self-sustained isothermal amplification. The amplified product is then used for RDH-LFA and signal is read after 5 minutes. (C) Agarose gel showing TMIRA products by using 10-fold serial dilutions of the synthetic target RNA (OE) as template with forward primer (T7-OE-F) and reverse primer tagged with biotin at 5'-end (OE-R-Biotin4). (d) RDH-LFA Colorimetric signal developed by using TMIRA OE amplicons derived from (C); RNaseP (Human) RNA was used as an internal positive control which was spiked at constant level in the target RNA (See text for details). (E) Evaluation of sensitivity and specificity of RDH-LFA coupled with TMIRA using clinical samples (see Supp figure S5): Scatterplot showing signal intensities of test spot in RDH-LFA with TMIRA for samples from both Covid-19 patients (positive) and healthy individuals (negative) as previously determined by standard commercial qRT-PCR method. Among 30 RNA samples previously tested positive with qRT-PCR, 29 samples were found to be positive using RDH-LFA. In the scatterplot, the blue dot refers to a positive result and red dot refers to a negative result, using RDH-LFA coupled with TMIRA.