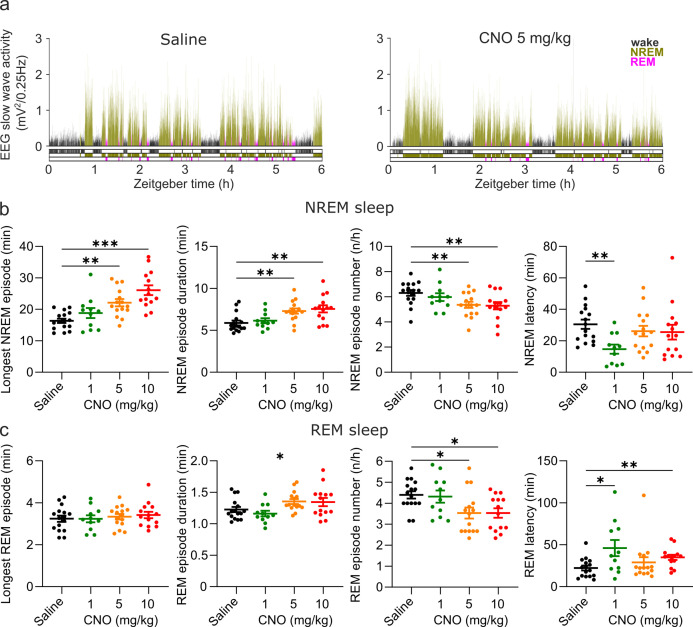
Figure 2. Altered sleep architecture following CNO injections.
(a) Representative hypnograms and EEG slow wave activity (0.5–4.0 Hz, 4 s epochs) from one individual mouse after injection of saline (left panel) and 5 mg/kg CNO (right panel). Note the reduced latency to NREM sleep, the suppression of REM sleep, and the increased duration of individual NREM sleep episodes. (b) NREM sleep architecture and (c) REM sleep architecture over the 6 hr observation period following saline and CNO injections. Note that for the average REM episode duration there is a main effect of ‘treatment condition’ but none of the individual post hoc comparisons between CNO and saline reaches the significance level of p=0.05. n=16 for saline, n=11 for 1 mg/kg, n=15 for 5 mg/kg, n=14 for 10 mg/kg for vigilance state analysis in panels b and c. Asterisks indicate post hoc comparisons with significant differences (*p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001) for analyses with significant main effects. CNO: clozapine-N-oxide. EEG: electroencephalogram. NREM: non-rapid eye movement sleep. REM: rapid eye movement sleep.