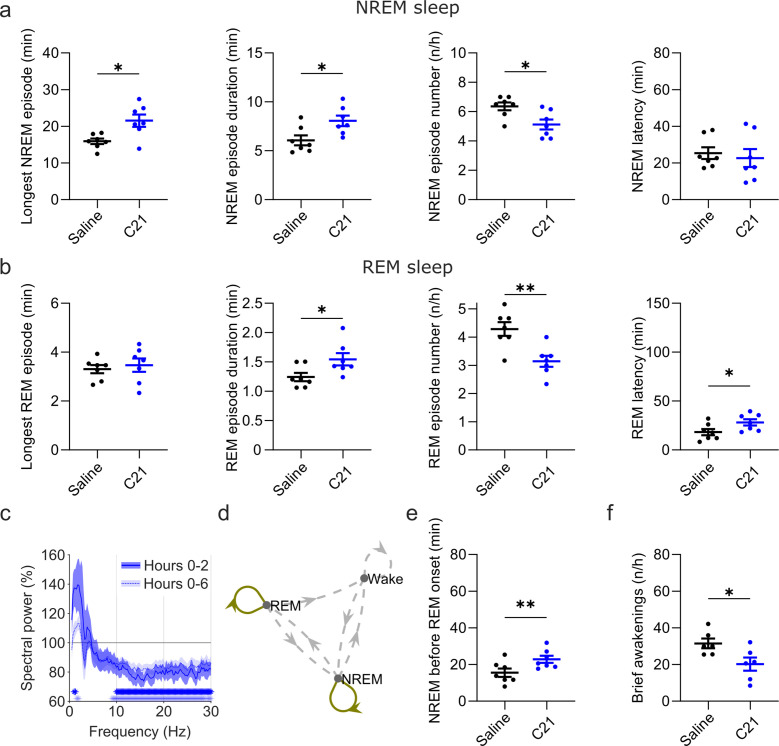
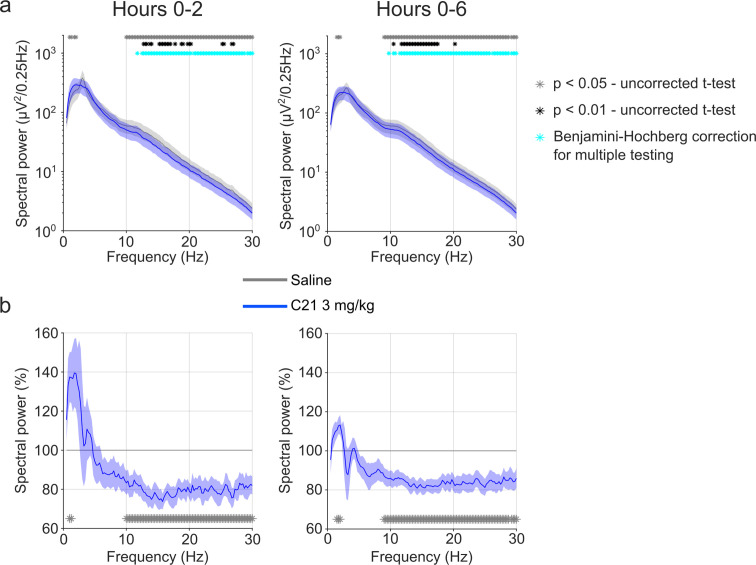
Figure 5. Effects of C21 on sleep architecture, NREM sleep spectra, sleep state stability, and sleep continuity resemble the effects of CNO.
(a) NREM sleep architecture and (b) REM sleep architecture for the 6 hr observation period following C21 injections. (c) Frontal EEG spectra during NREM sleep relative to saline injections for the acute (first 2 hr, dark blue) and full (6 hr, light blue) observation period following C21 injections. Asterisks indicate frequency bins with significant differences in post hoc comparisons using uncorrected paired t-tests (p<0.05; acute: dark blue, full: light blue) following a significant interaction effect between ‘frequency’ and ‘condition’ in two-way ANOVAs. (d) Transitions between vigilance states in the 6 hr period following saline and C21 injections. Note the increased stability of REM and NREM sleep (REM>REM: p=0.0144, Cohen’s d=1.0325; NREM>NREM: p=0.0384, Cohen’s d=0.81527). Solid olive lines indicate significantly increased transitions/continuations of vigilance states in the C21 condition compared to the saline condition, dashed grey lines indicate all possible vigilance state transitions/continuations. (e) Cumulative amount of NREM sleep before the first occurrence of REM sleep. (f) Frequency of brief awakenings (4–16 s) per hour of sleep for the first 2 hr after injections. Number of animals n=7 mice for vigilance state analysis in panels a, b, d, and e. For analysis of EEG NREM spectra in panel c and brief awakenings in panel f: n=6 mice. Asterisks in panels a, b, e, and f indicate t-tests with significant differences (*p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001). Data in c are presented as the mean ± s.e.m. (shaded areas). ANOVA: analysis of variance. C21: compound 21. EEG: electroencephalogram. NREM: non-rapid eye movement sleep. REM: rapid eye movement sleep.