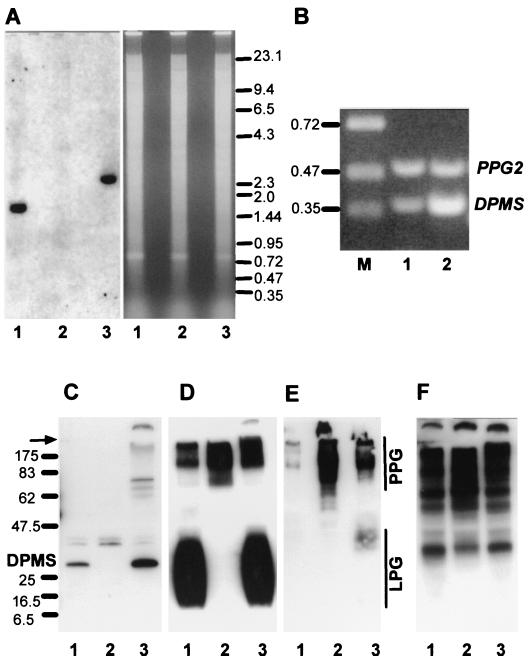
FIG. 8.
Analysis of L. mexicana wild type, a ΔDPMS mutant, and a DPMS gene addback mutant by Southern blotting, RT-PCR, and immunoblotting. (A) Southern blot analysis of SalI restriction enzyme-digested chromosomal DNA (10 μg) from L. mexicana wild type (lanes 1), a ΔDPMS mutant (lanes 2), and a ΔDPMS + cRIBDPMS gene addback mutant (lanes 3). The digested DNAs were separated on an ethidium bromide-containing 0.7% agarose gel (right), blotted onto a nylon membrane, and incubated with a DIG-labeled DPMS ORF probe (left). The sizes of DNA standards are indicated in kilobases. (B) Amplification of DPMS mRNA from L. mexicana log-phase promastigote (lane 1) and amastigote (lane 2) by RT-PCR from total RNA. The loading was normalized to the coamplified cDNA fragment derived from the PPG2 gene, whose mRNA is approximately equally abundant in L. mexicana promastigotes and amastigotes (13). The sizes of DNA standards are indicated in kilobases. (C to F) SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting of L. mexicana wild-type, ΔDPMS mutant, and DPMS gene addback total promastigote lysates. Lane 1, wild type; lane 2, ΔDPMS; lane 3 ΔDPMS + cRIBDPMS. Each lane was loaded with 106 promastigotes (∼4 μg of protein). (C) Blots probed with affinity-purified rabbit anti-L. mexicana DPMS antibodies. The same or identically loaded blots were then stripped and probed with MAb LT6 (directed against [6Galβ1-4Manα1-PO4]x) (D), MAb LT17(directed against [6(Glcβ1-3)Galβ1-4Manα1-PO4]x [x = unknown]) (E), and MAb L7.25 (directed against [Manα1-2]0-2Manα1-PO4) (F). The molecular masses and relative positions of standard proteins and the positions of DPMS, LPG, and PPG are indicated. The arrow marks the borders between stacking and separating gels.