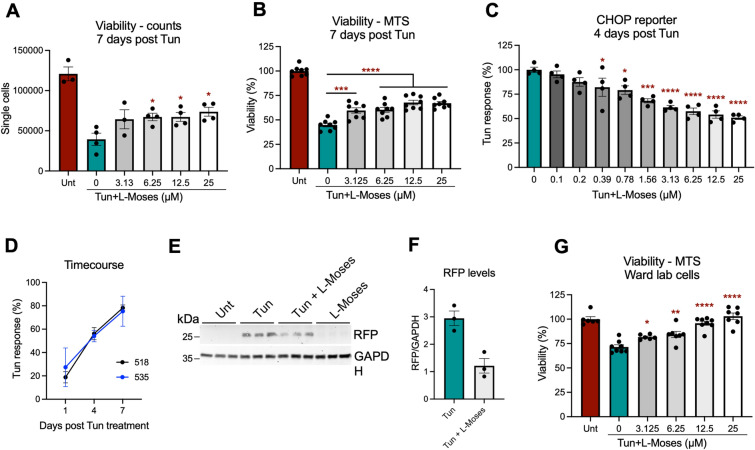
Figure 4.
L-Moses attenuates Tun-mediated effects on cortical neurons. (A,B) Co-treatment with L-Moses significantly increases viability of 100 nM Tun-treated samples, as judged by cell counting (A) and MTS assay (B). (C) L-Moses reduces Tun-mediated response (Tun-treated minus Unt MFI) in the CHOP reporter lines, in a dose-dependent manner. (D) Time-course showing that L-Moses effect is reduced with continuous exposure to 100 nM Tun, using both homozygote clonal lines (518 and 535). (E,F) Western blot confirming reduces RFP levels in Tun + L-Moses treated samples, when compared to Tun-treated. Original blots are presented in Supplementary Fig. S7. (G) Significant rescue in viability, following L-Moses treatment, was observed in cortical neurons derived from an independent iPSC cell line (Ward lab). One-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 and ****p < 0.0001 compared to 100 nM Tun only control (blue bar).