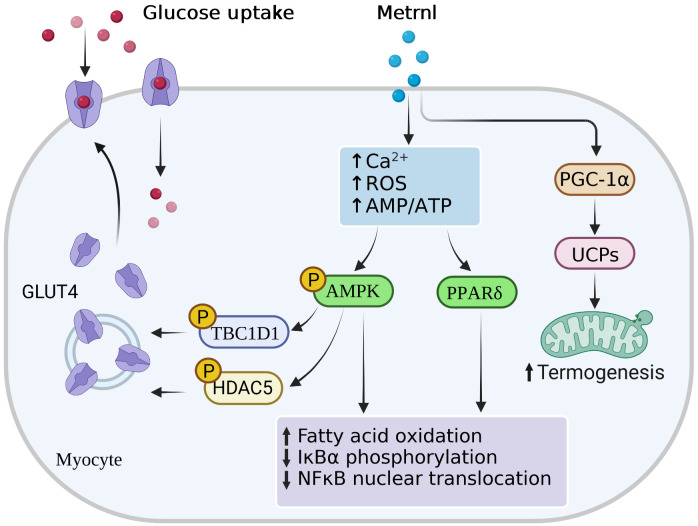
Figure 2.
Main signal pathways of Metrnl in myocytes. Metrnl could activate AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-δ (PPAR-γ) signaling by increasing intracellular calcium ion, reactive oxygen species (ROS), or AMP/ATP ratio levels in skeletal muscle cells. Activation of AMPK phosphorylation stimulated phosphorylation of HDAC5 and TBC1DI, both of which resulted in the GLUT4 transcription activation and translocation from the cytoplasm to the membrane. Highly PPAR-γ expressions and AMPK phosphorylation increased fatty acid oxidation, IκBα phosphorylation, and NFκB nuclear translocation. Besides, Metrnl also increased intramuscular PGC-1α and UCPs expressions, thus promoting mitochondria thermogenesis.