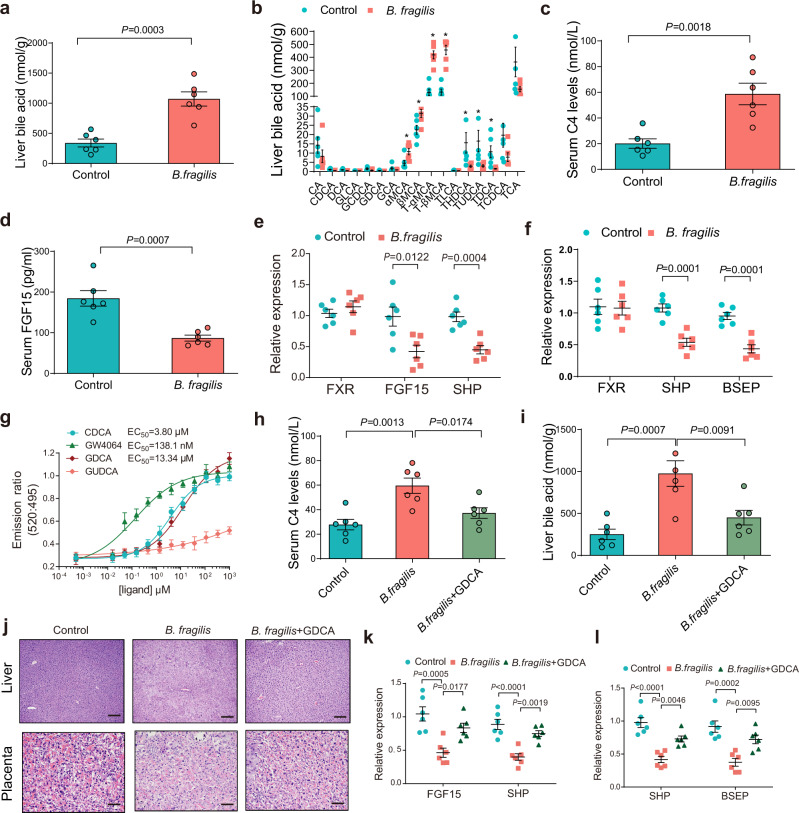
Fig. 4. B. fragilis suppressed FXR signaling through mediating bile acid metabolism to increase hepatic bile acids accumulation.
a Liver total bile acid levels in B. fragilis transplanted mice or control group (n = 6 per group). b Hepatic bile acids profiles in B. fragilis transplanted mice or control group (n = 6 per group). P values were determined by two-tailed Student’s t-test for a, b. *P < 0.05. c, d Serum C4 levels (c) and FGF15 levels (d) in B. fragilis transplanted mice or control group (n = 6 per group). P values were determined by two-tailed Student’s t-test. e, f Relative expression of intestinal (e) and hepatic (f) FXR mRNA and its target genes in mice colonized with B. fragilis or control (n = 6 per group). P values were determined by two-tailed Student’s t-test. g TR-FRET FXR coactivator recruitment assay to assess the action of GDCA on FXR; CDCA and GW4064 was used as positive control. GUDCA was used as negative control (n = 3 per group). h Serum C4 levels in each group (n = 6 per group). i Liver total bile acid levels in each group (n = 6 per group). P values were determined by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s correction for h–j Representative images of H&E staining of livers and placenta in each group. Scale bar = 100 μm for liver; scale bar = 50 μm for placenta. k, l Relative expression of intestinal FXR target genes (k) and hepatic FXR target genes (l) in indicated groups. n = 6 per group. P values were determined by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s correction. Data are presented as mean ± SEM for a–i, k, l. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.