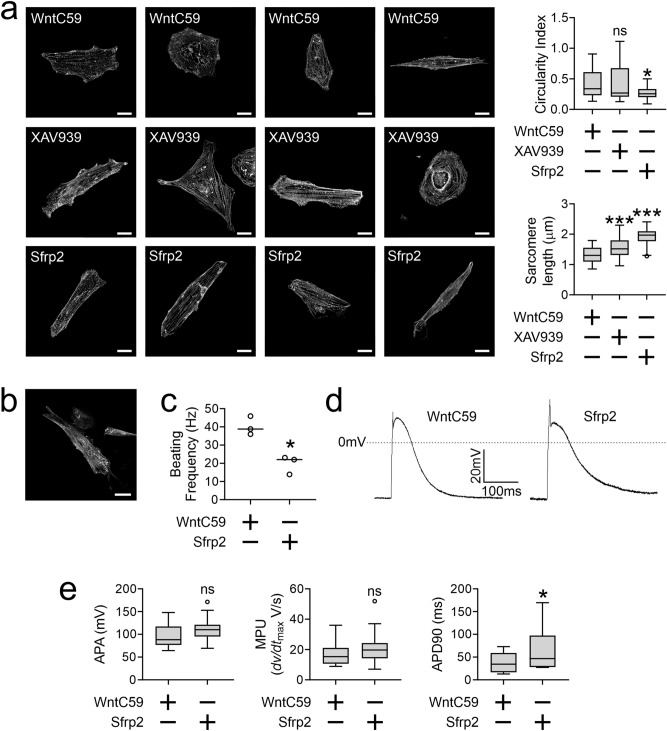
Figure 2.
Sfrp2 improves iPSc-derived cardiomyocyte maturation. iPSc were differentiated into cardiomyocytes via the standard broad-spectrum Wnt inhibitor (WntC59, XAV939) method or via the Sfrp2 method. Cells were analyzed on day 14 of differentiation protocol. (a) cells were fixed and stained with an antibody targeting α-Actinin (Actn2). Left hand side: Representative images shown (scale bar 20 microns). Right hand side: Quantification of two parameters of maturation: circularity and sarcomere length. N > 30 for each group. Comparisons are made to the WntC59 group: ***P < 0.001, *P < 0.05, ns-not significant. (b) Representative image of a Sfrp2-derived cardiomyocyte after 40 days in culture. Scale bar 20 microns. N = 3. (c) Beating frequency was determined on day-14 of the differentiation protocol by measuring the number of contractions over a 20 s period. For each experiment, 3 wells were analyzed. Representative experiment shown. *P < 0.05. (d) Fourteen days after the start of differentiation, patch-clamp was performed. Sample action potentials of cardiomyocytes generated via the standard broad-spectrum Wnt inhibitor (WntC59) approach or via Sfrp2 protocol. (e) Patch-clamp data was analyzed for action potential amplitude (APA), maximal rate of depolarization (MPU) (dv/dtmax ( and action potential duration (APD) at 90% of APA. N = 15 (WntC59) or 19 (Sfrp2). Comparisons were made to the WntC59 group: *P < 0.05, ns – not significant.