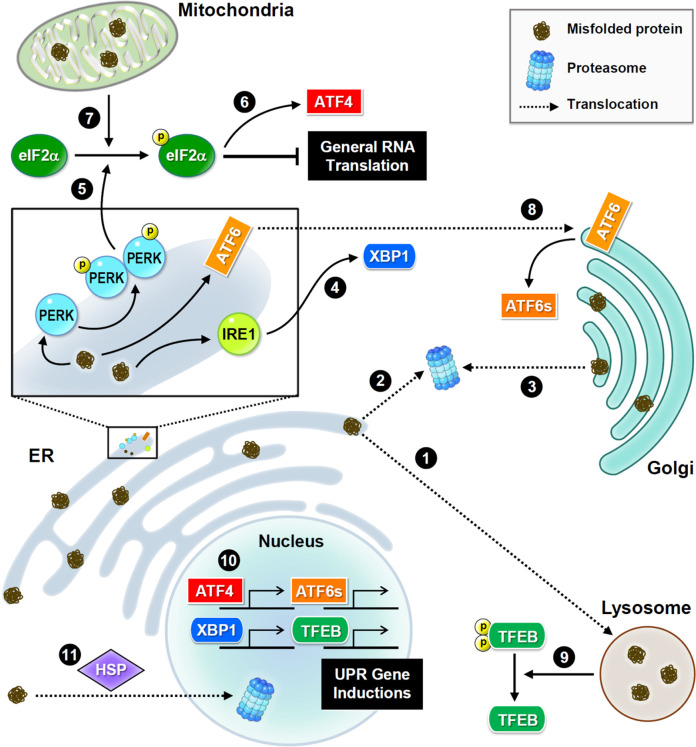
FIGURE 2.
Subcellular proteostasis and UPR signaling. Schematic presentations of proteostasis signaling and protein trafficking in distinct organelles. Main stress sensors and transcription factors are presented. Misfolded proteins are transferred between the ER and Golgi apparatus for refolding, or to the lysosome or nucleus for degradation. In the ER, three major UPR signaling pathways trigger proteostatic processes. First, PERK phosphorylates eIF2α to inhibit the assembly of the initiation ternary complex, thereby suppressing general translation. Additionally, mitochondrial damage also induces phosphorylation of eIF2α. Conversely, some proteins such as transcription factor ATF4 are preferentially produced. Second, IRE1 mediates RNA splicing and promotes the synthesis of transcription factor XBP1. Third, ATF6 is transferred to the Golgi apparatus and cleaved into a short and active form. Furthermore, the proteome stress dephosphorylates and activates transcription factor TFEB. Together, these transcription factors drive the induction of UPR genes to ensure proteostasis.