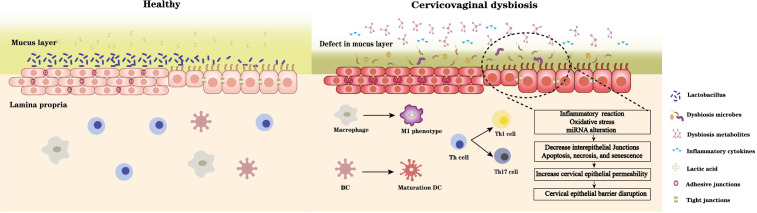
Figure 1.
A healthy Lactobacillus dominant microbiota and the acidic environment formed by the associated metabolites especially lactic acid maintain cervical epithelial barrier integrity, stabilise the mucosal immune system. In contrast, microbiota dysbiosis and its accompanying changes in microbial metabolites can 1) damage mucus layer; 2) imbalance immune system: promote immune cells differentiate towards proinflammatory type and induce pro- and inflammatory cytokines secretion; 3) disrupt cervical epithelial barrier: induce inflammation reaction, oxidative stress, miRNA alteration of cervical epithelial cell, decrease intracellular junctions, and promote cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, and necrosis. Thus, increase the epithelial permeability and disrupt barrier function.