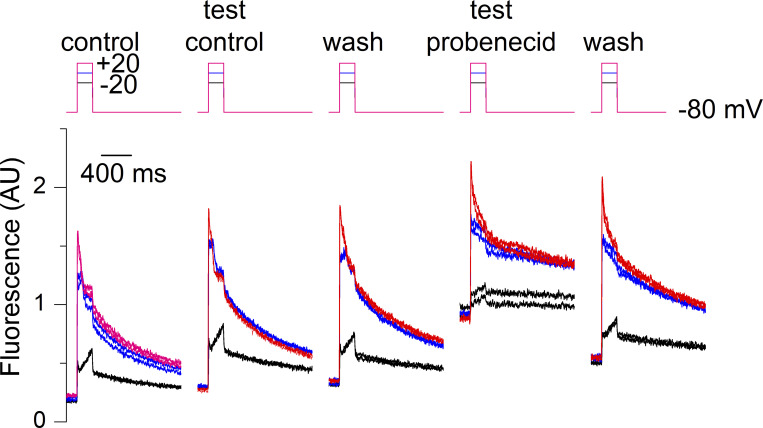
Figure 5.
Effect of a transient application of probenecid on voltage-activated Ca2+ transients in a muscle fiber. Rhod-2 Ca2+ transients elicited by the pulse protocol shown on top upon successive changes in the extracellular solution. Each depolarizing pulse was repeated twice to check for the stability of the response. From left to right, rhod-2 transients elicited by 200 ms-long pulses to −20, 0, and +20 mV (1) in the initial control condition, (2) during the test-control condition, (3) after wash out (wash), (4) after application of the probenecid-containing solution, and finally after probenecid wash-out. Throughout the control measurements, the resting rhod-2 fluorescence level tended to slightly increase with time because of the not-entirely-complete (1) equilibration of the pipette solution with the cell interior and (2) recovery of the resting fluorescence following a voltage-activated transient.