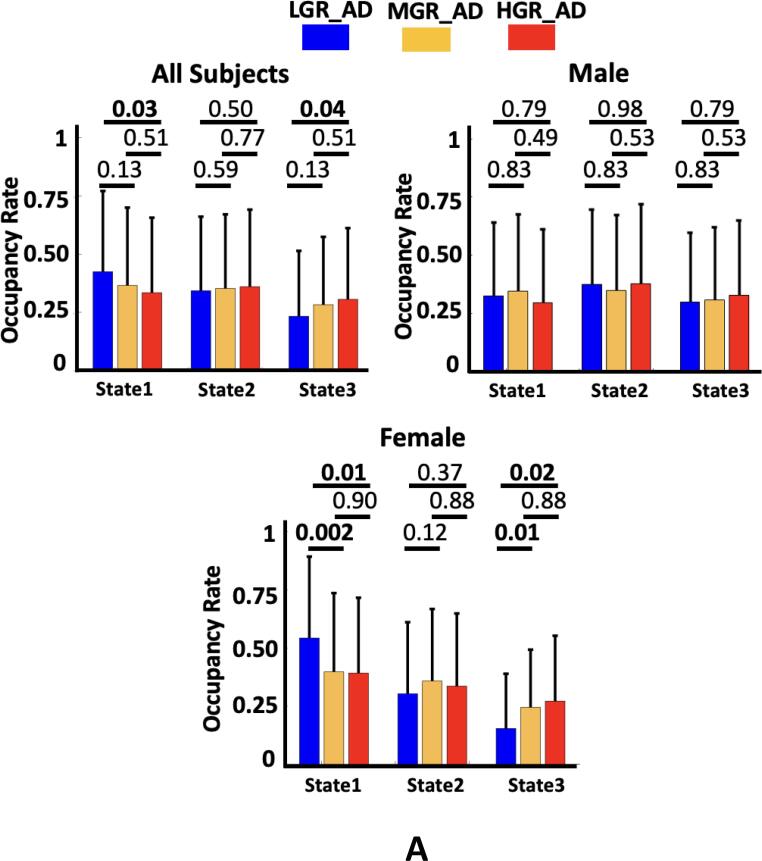
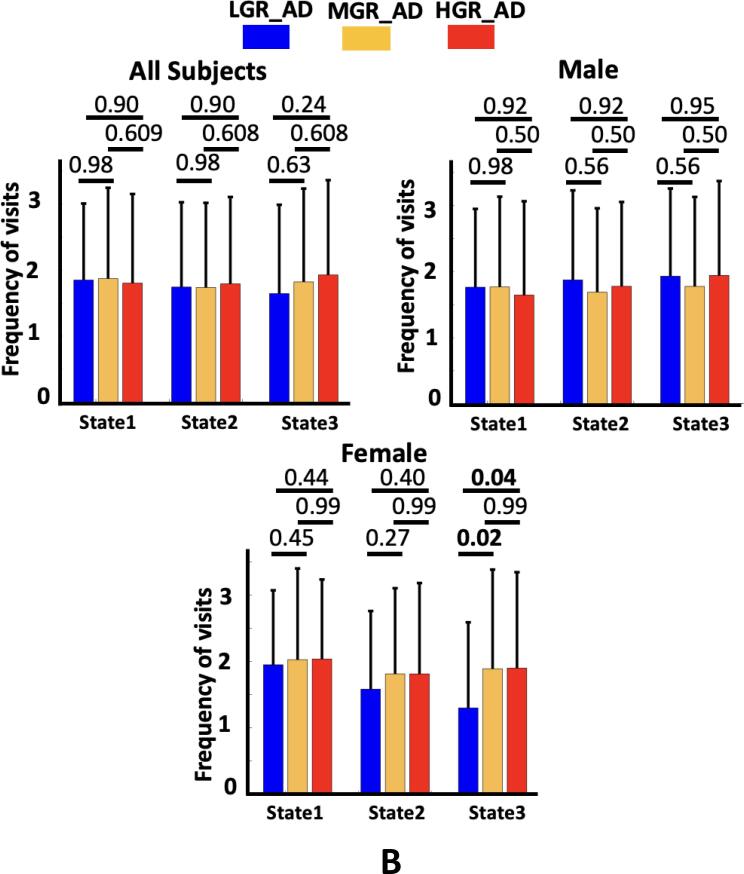
Fig. 5.
Genetic risk effects on dFNC features. A) The occupancy rate (OCR) of each group in state 1, state 2, and state 3. All individuals: The individuals with the ɛ2 allele spent more time in state 1 than those individuals without the ɛ2 allele (corrected p < 0.05). Male: The occupancy rate (OCR) of each group in state 1, state 2, and state 3. No significant difference was observed among the groups. Female: The occupancy rate (OCR) of each group in state 1, state 2, and state 3. The individuals without the ɛ2 allele spent more time in state 3 than those individuals with the ɛ2 allele (corrected p < 0.05). B) The frequency of visits to states 1, state 2, and state 3. All individuals: No significant difference was observed across the group. Male: No significant difference was observed among the groups. Female: participants with the ɛ2 allele have fewer visits to state 3 than those with the ɛ3 and ɛ4 alleles (corrected p < 0.05). LGR-AD: Low genetic risk of AD, MGR-AD: Moderate genetic risk of AD, HGR-AD: High genetic risk of AD. The error bars represent the standard deviation.