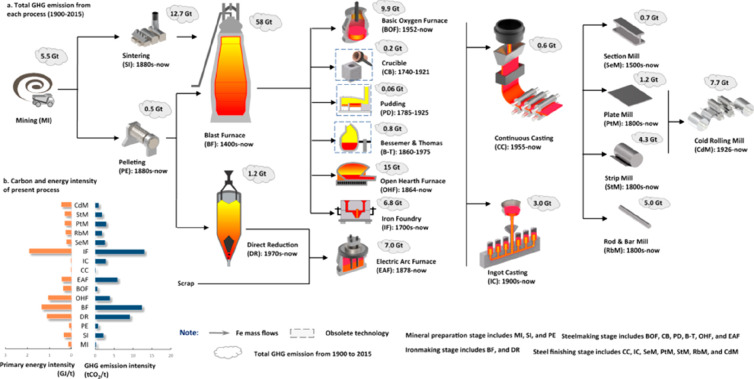
Figure 119.
Wang et al.463 studied the process-specific origin in greenhouse gas emissions from the traditional steel industry for the years 1900 to 2015. They found that the substantial efficiency improvements, by up to two-thirds for some of the processes, were overcompensated largely by very carbon-intense steel production methods employed in emerging industry regions, so that the total net emissions have stagnated since 1995. (a) Main process steps and total carbon emissions from 1900 to 2015. (b) Energy intensity and carbon intensity level for each process (details are given in the original paper463). MI, mining; SI, sintering; PE, pelleting; BF, blast furnace, DR: direct reduction, BOF: basic oxygen furnace, CB: crucible, PD: puddling; B-T, Bessemer & Thomas; OHF, open-hearth furnace; IF, iron foundry; EAF, electric arc furnace; CC, continuous casting; IC, ingot casting; SeM, section mill; PtM, plate mill; StM, strip mill; RbM, rod bar mill; CdM, cold rolling mill. The figure is reproduced from ref (463) with permission. Copyright 2021, Springer Nature.