Figure 22.
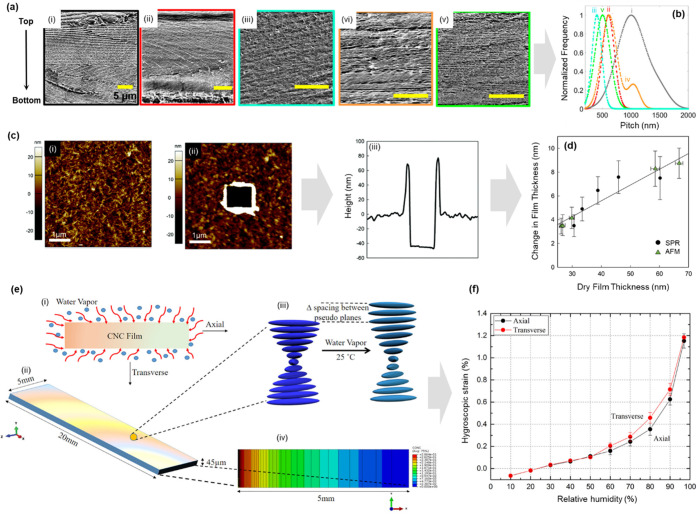
Nanocellulose–water interactions revealed by microscopic techniques: (a) SEM images of the cross-section of pristine CNCs (i) fast-dried, (ii) slow-dried, (iii) slowest-dried, and MePh3P-modified CNCs (iv) fast-dried, and (v) slow-dried. Scale bars = 5 μm.1016 (b) Nominal pitch distributions measured from SEM images of films (i–v).1016 (a,b) Adapted with permission from ref (1016). Copyright 2017 American Chemical Society. (c) AFM height image of a dry CNC film (i) which was scratched (ii) for cross-section height analysis (iii) to determine the film thickness.284 (d) Change in CNC film thickness in water determined by AFM and SPR (solid line for eye guidance).284 (c,d) Adapted with permission fromref (284). Copyright 2009 The Royal Society of Chemistry. (e) Scheme representing CNC film moisture sorption. (i) moisture diffusion into the film, (ii) 3D scheme of the CNC film for moisture diffusion analysis by cross-polarized microscopy, (iii) interspace between the CNCs increasing upon water penetration, and (iv) simulation contour of moisture diffusion after 15 h.331 (f) Hygroscopic strain, obtained by digital image correlation, as a function of the RH for self-organized CNC films for axial (black) and transverse (red) directions.331 (e,f) Adapted with permission from ref (331). Copyright 2017 American Chemical Society.