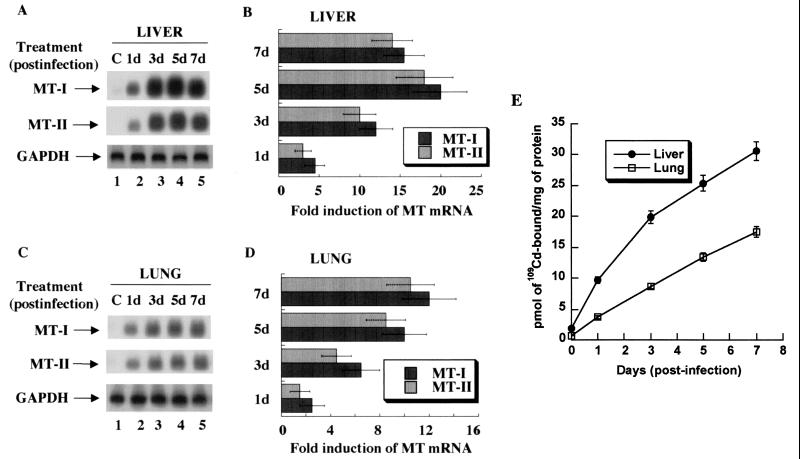
FIG. 1.
Time-dependent expression of MT-I and MT-II mRNA and proteins in the liver and lung of C57/BL6 mice infected with the influenza A virus. Total RNA (15 μg) was separated on a denaturing agarose (1.2%) gel, transferred to Hybond N+ membrane, and hybridized to 32P-labeled oligonucleotide antisense to mouse MT-I and MT-II mRNAs or rat glyceroldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) cDNA. (A) Northern blot analysis of MT-I and MT-II expression in the liver. (B) Induction level of MT-I and MT-II mRNAs. (C) Northern blot and (D) quantitative analyses of MT expression in the lung. The fold induction in the liver or lung is estimated by taking the basal value in the control tissue as 1. Results are the means of three independent experiments ± standard error of the mean (SEM). (E) 109Cadmium binding activity of MTs. One hundred micrograms of protein of the liver and lung extracts from the control and infected animals was heated in a boiling water bath, and the denatured proteins were removed by centrifugation. The supernatant was incubated with 109CdCl2 under optimum binding conditions, excess free cadmium was removed by adding hemoglobin and heat denaturation, and heat-stable Cd-MT was measured by gamma counter. The data are the mean values from the extracts obtained from five animals ± SEM. Each extract was assayed in triplicate. The plot was generated using the Kaleidagraph program.