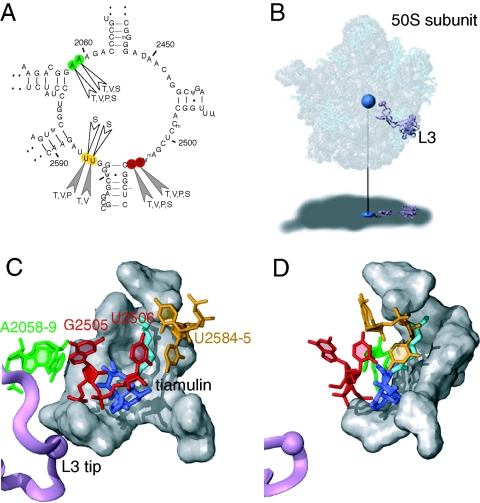
FIG. 3.
Ribosomal binding site of the pleuromutilin antibiotics. (A) Secondary structure of domain V of E. coli 23S rRNA, showing the chemical footprints of the four pleuromutilin antibiotics in color (A2058 and A2059 in green, G2505 and U2506 in red, and U2584 and U2585 in yellow). The nucleotide positions exhibiting altered reactivities in the presence of each drug (T, tiamulin; V, valnemulin; P, pleuromutilin; and S, SB-264128) are indicated. Protection effects are shown as filled arrowheads and enhancement effects as open arrowheads. (B) The structure of the 50S subunit from Deinococcus radiodurans complexed with tiamulin (15) (PDB accession no. 1XBP), where tiamulin is represented as a blue sphere and ribosomal protein L3 as a purple ribbon. RNA is represented as gray spheres, and proteins are shown as light blue ribbons. The subunit is rendered transparently to show the internal positions of tiamulin and L3, which are projected onto the shadow below. (C) An expanded view of the tiamulin binding site. Tiamulin is shown in stick representation, where the mutilin core is in dark blue and the side chain extension is in cyan. The nucleotides in the footprints and L3 are colored as described for panels A and B. Other nucleotides involved in hydrophobic interactions with tiamulin (15) are shown in gray. (D) As in panel C, but rotated 60 degrees around the y axis.