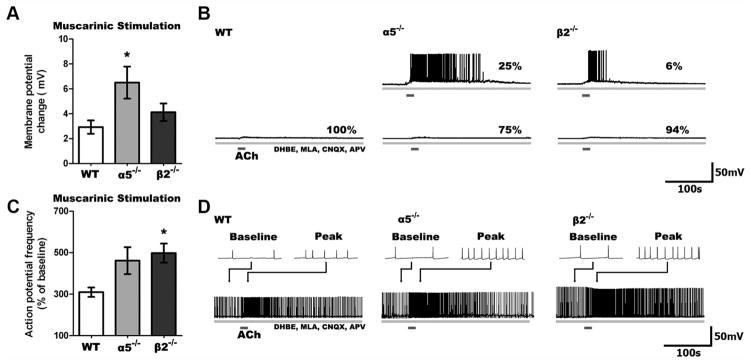
Figure 3.
Muscarinic responses are enhanced in α5 −/− and β2 −/− compared to WT neurons. A, Stimulation of only muscarinic receptors on layer VI neurons following blockade of nicotinic receptors (3 μM DHBE, 10 nM MLA) and glutamate receptors (10 μM CNQX, 50 μM APV) resulted in significant differences in depolarization across genotypes (p <0.05), with greater muscarinic depolarization seen in α5 −/− than WT neurons (*p <0.05). B, Sample traces show the muscarinic response in neurons from all genotypes. No WT neurons, but some α5 −/− and β2 −/− neurons are depolarized to threshold. C, Muscarinic stimulation increases action potential firing differently across the genotypes (p <0.001), with action potential frequency increasing to a greater degree in β2 −/− compared to WT neurons (*p <0.05). D, Sample traces showing muscarinic responses in neurons depolarized to fire action potentials by current injection.